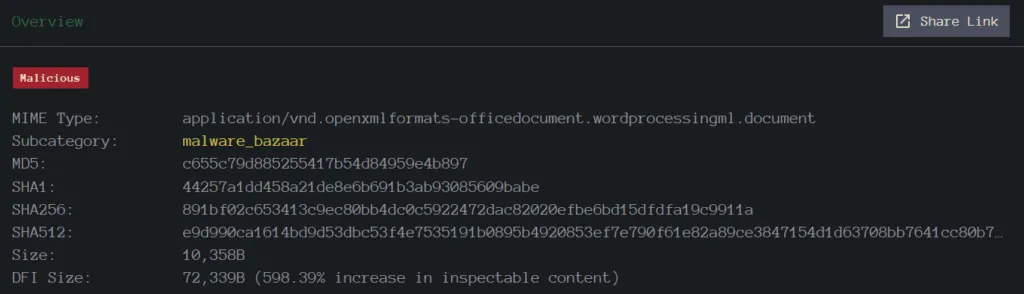
Distribution of LokiBot
This article introduces the latest wave of VBS LokiBot campaign, and it’s subsequent analysis by LMNTRIX. One of the most prevalent malware families that the LMNTRIX CDC has recently seen is called LokiBot. It targets hundreds of computer programs installed on the compromised system, including commonly used web browsers, email clients, and FTP servers, in order to steal sensitive information from the target like usernames, passwords, and cryptocurrency wallets.
Our technical analysis suggests that it was likely produced in one of the former USSR states (Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, and Belarus). The LokiBot malware’s most recent samples are propagated through malspam campaigns that encourage recipients to download infected file attachments. It is frequently used to spread the infection through a wide range of methods, including sharing Microsoft Office documents or script files that are designed to download and install additional malware payloads, including archive files containing an ISO file or a LokiBot executable.
Infection Chain
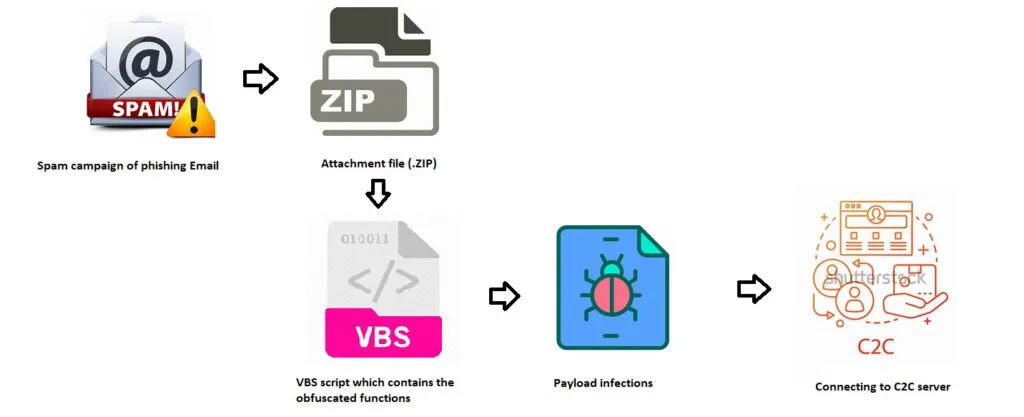
Lokibot infects its victims by initial infection vectors of spam emails. This kind of email file gets delivered in password-protected archives, which contains a JavaScript file. Usually, these .JS files are embedded with malicious URL to download the payload file, likewise it uses known infection from [tgcXXX.XXXX] domain in-order to download the payload files.
The initial vectors may vary depending on the individual threat actor and their targets, we all know that the threat actors will perform basic reconnaissance, when he targets a certain geography prior to choosing the infection vector.
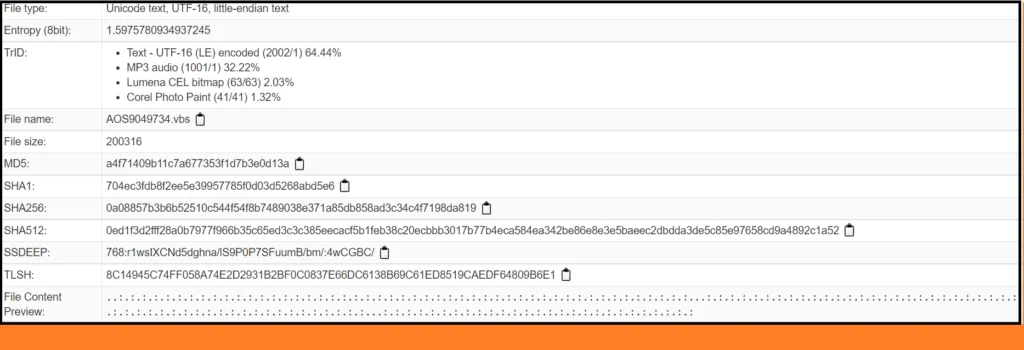
Sample Information
SHA256: 0a08857b3b6b52510c544f54f8b7489038e371a85db858ad3c34c4f7198da819
Technical Analysis of Lokibot VBS Campaign
VBS (Virtual Basic Script) file is an interpreted scripting language which contains code that can be executed within Windows or Internet Explorer, via the Windows-based script host (Wscript.exe), to perform certain admin and processing functions. Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) code can be included as a part of the file header and footer properties (Left-Header, Center-Header, Right-Header, Left-Footer, Center-Footer, and Right-Footer). This is very helpful for an analyst when analyzing any script file / script based malware.
Snap 1: Header Content
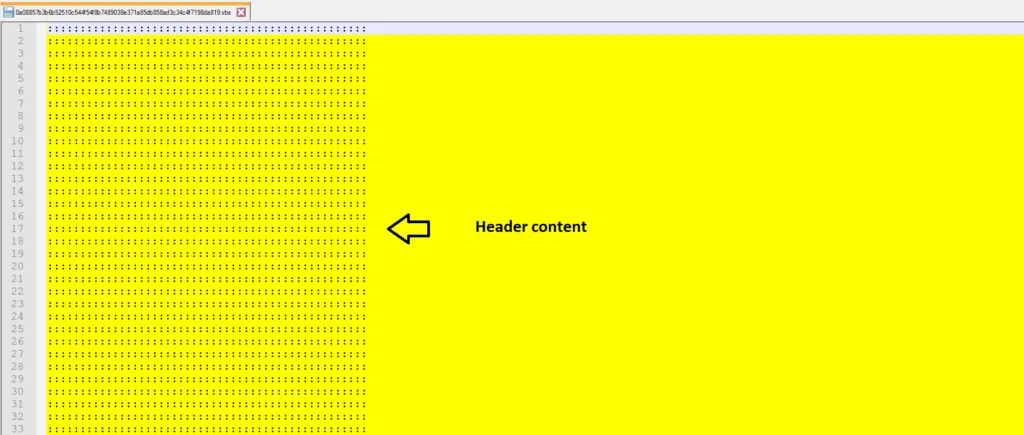
Our sample contains a header content of dotted element. With these tricks, can we analyze the sample adequately?? Probably not. The malware author dupes the target to believe there’s no hidden content inside the file. Let’s examine the footer content of our sample and, then we can start our analysis.
Snap 2: Footer Content
Snapshot shown above was taken from the sample’s footer content. This section also contains the dotted elements (padding). Does it mean it’s a legitimate file??
The embedded content was really deftly placed in the centre of the file by the malware author, the main reason is to facilitate AV evasion, or to avoid being detected by the AV vendors. Just observe the header’s starting line and ending line, almost 2000 lines, the author chooses to pad the centre of the file with dotted lines to hide the malicious content.
Snap 3: Middle content
Snap 4: Embedded Content
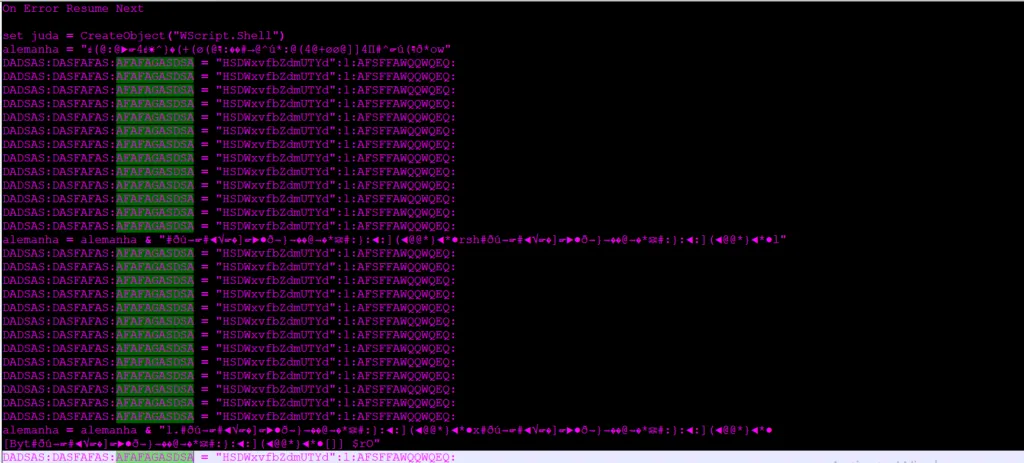
From the snapshot seen above, we can observe a function inside the file is obfuscated. Upon additional analysis, we should be able to predict & replace the content exactly.
Snap 5: Embedded Content with URL
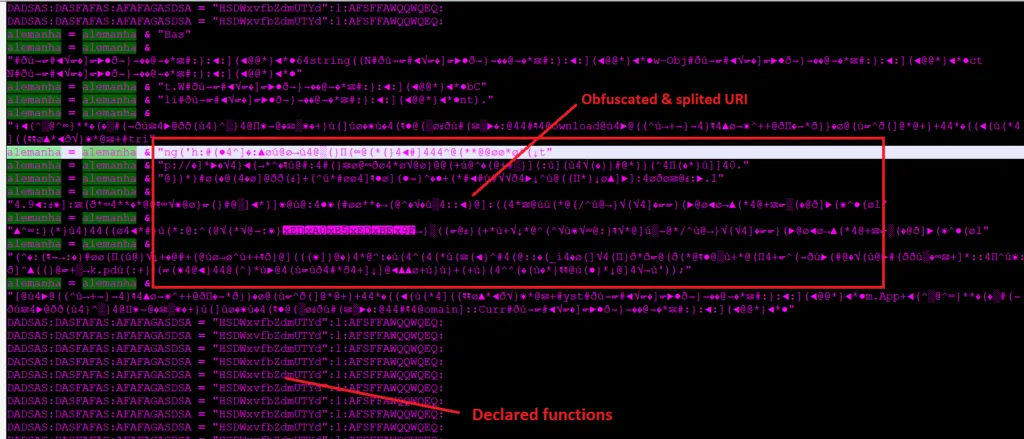
With further analysis, LMNTRIX CDC is able to predict the multi-part URL, and it’s declared functions.The URL is split into smaller parts and rejoined to avoid detection, another manoeuvre in every modern malware author’s bag of tricks. Using the destination URL, it will download the payload file and store it in the Windows’ %AppData% folder.
Snap 6: Threat Identifiers

Snap 7: Initial – Indicator of Compromised [IOC]
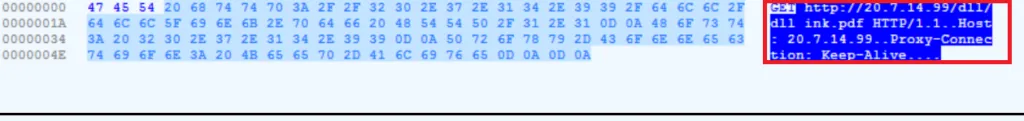
It’s the common IOC of Loki-Bot, where it’s used for a long period. Using this URL it will connect with the threat actor’s C2 server.
Once the system is infected, Lokibot will perform the following actions:
- Collecting information about the compromised host.
- Password stealing (from browser history and cookies).
- Targeting web banking links (web injects).
- Password brute forcing.
- Registry manipulation (persistence).
- Replicating its copies.
- Process injection to conceal the malicious action.
Appendix A – LokiBot Components
These are possibly the files (file artefacts) hidden within the Windows %APPDATA% directory at any given point in time. LMNTRIX has outlined the functions of the files dropped by Loki Bot campaign,
| File Extension | File Description |
| .exe | An executable copy of the malware that will execute each the user account is logged into |
| .hdb | Database of hashes for data that has already been exfiltrated to threat actor’s C2 server |
| .kdb | Database of keylogging data that has yet to be sent to the C2 server |
| .lck | A lock file created when either decrypting windows credentials, or, keylogging to prevent resource conflicts on Windows |
| .vbs | Staged shellcode or, malicious loader to execute functions of the Lokibot campaign |
Appendix B – Indicators of Compromise for LokiBot
IP Address
210[.]245[.]8[.]133
212[.]1[.]211[.]48
172[.]67[.]179[.]121
23[.]253[.]46[.]64
31[.]170[.]160[.]61
74[.]208[.]236[.]199
162[.]241[.]3[.]30
172[.]67[.]206[.]17
204[.]93[.]178[.]31
216[.]10[.]240[.]90
103[.]26[.]43[.]131
78[.]128[.]76[.]165
212[.]108[.]234[.]94
172[.]67[.]214[.]235
104[.]18[.]39[.]232
50[.]31[.]174[.]86
77[.]222[.]62[.]31
104[.]18[.]32[.]77
172[.]67[.]204[.]22
103[.]199[.]16[.]121
Hashes Observed
E9E14BAF4ADF6E1D45016C79EC09B7E5A36E1DEE272E1F335F96CE7CDFED127A
51F462CFFF7CCE2803C70069E302A86C66F43CEC35602171A4752A997013CA87
442730F6CF2A2FF1D7CA9E286F5BDCF99689CAE3C8B959F9B1DBBDDD6839F78A
52431707738F4962E6D465B66C5A8D56D36B0EDBCBC268002BC56C6F4B40A4D2
958595E2B49E0042FC6888D3CD008DCA5FD38BC79CD7574DD5031B27171ED811
A822B982EF431F0A6813EF38DD672151C786AADB71C0787F8419BD04B127A44D
DA65AEE4D8D8B4F979AB4176C9E69347E06187EF59C03914F278859ACADFF45A
AE4AD82FDBD7BE97E93A92555320E683EA177DE299F4A882411D652B464837F7
D361D688E58FAFB99967AFC805BD203C1F743A113B8C76C7E94B2960F40B285D
D072A28D28A7498F48B82D55BE214F4808F18EAEB1CBD6E414BD131CB507FC04
0D3E3B77F530D1D4AE4ABC3AC74283EA6E6FF41784A14447E925EE88E6D057C5
77C100C1960321C3FA9BE5157FB9F9E21D9C0AB60D1106DF819E431516462CE4
107B6B206140ED200F6440F30077C53ED7DB2447C04CDE954C52437962EA0FCB
050A053B4F14B010CFC82949BB761C209D1B4A8E98675E1E13FE072EF942B246
839119DE734C39B0C2F3C1391AED1F9F5BC6BD162DF9194743CF3EC6AF90BEF8
F172723AA5C023E6D22BDBBFA8DE48679C694AF6EAF6156142BABF4913F520CE
542219BA546FB9770B914CBC0F7FA117C1CF3FC2F8C4D58165E4884328196ABA
E4D40B456C9DA36ED8516C0B5A77819368020F6D386ED8955814CA77FFF5F58A
73B13CEA2C234CE674DAE5666BC66FE01BA387283672CCF2684735A1B8C9A643
Domains
data[.]jsdelivr[.]com
secureanalytic[.]com
ww1[.]tsx[.]org
ww1[.]virustoal[.]com
majul[.]com
css[.]developmyredflag[.]top
www[.]downloadnetcat[.]com
cdn[.]intedia[.]de
cdn[.]siteswithcontent[.]com
mail[.]tecniagro[.]net
kucukkoybutik[.]com
makemyroster[.]com
guose[.]intsungroup[.]com
app-a[.]customericare[.]com
mail[.]forumsboard[.]com
www[.]sgstockexpert[.]com
pnpboxes[.]com
wolneatomy[.]com
smtp[.]standardsintered[.]com
www[.]harbygazete[.]com
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping for Loki Bot
According to MITRE, the Loki Bot uses the following, tools tactics and procedures,
| Tactics/Techniques (TTP) | Malware Function |
| System Network Configuration Discovery [T1016] | LokiBot has the ability to discover the domain name of the infected host. |
| Obfuscated Files or Information [T1027] | LokiBot has encoded strings with base64 encoding. |
| Obfuscated Files or Information: Software Packing [T1027.002] | LokiBot has used several packing methods for obfuscation. |
| System Owner/User Discovery [T1033] | LokiBot has the ability to discover the system information and username on the infected host. |
| Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041] | LokiBot has the ability to initiate contact with command and control to exfiltrate stolen data. |
| Process Injection: Process Hollowing [T1055.012] | LokiBot has used process hollowing to inject into legitimate Windows process vbc.exe. |
| Input Capture: Keylogging [T1056.001] | LokiBot has the ability to capture input on the compromised host via keylogging. |
| Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001] | LokiBot has used Hypertext Transfer Protocol for command and control. |
| System Information Discovery [T1082] | LokiBot has the ability to discover the computer name and Windows product name/version. |
| User Execution: Malicious File [T1204.002] | LokiBot has been executed through malicious documents contained in spear phishing email. |
| Credentials from Password Stores [T1555] | LokiBot has stolen credentials from multiple applications and data sources including Windows operating system credentials, email clients, File Transfer Protocol, and Secure File Transfer Protocol clients. |
| Credentials from Password Stores: Credentials from Web Browsers [T1555.003] | LokiBot has demonstrated the ability to steal credentials from multiple applications and data sources including Safari and Chromium and Mozilla Firefox-based web browsers. |
| Hide Artifacts: Hidden Files and Directories [T1564.001] | LokiBot has the ability to copy itself to a hidden file and directory. |


