Introduction
ISFB (URSnif, also known as Gozi), is one of the most widely spread banking trojans – it is aimed to steal the banking credentials and commonly targeting the corporate users. The malware was among the Top 10 malicious strains to infect the healthcare industry. ISFB/Ursnif has undergone several development iterations since its source code was leaked in 2015/16.
Other Names: RM3, Ursnif, Dreambot, CRM, and Snifula, Gozi can be considered as a group of malware families which are based on the same malicious codebase. Historically, it has been known as one of the most widely spread and longest-standing Banking Trojans with more than 14 years of malicious activity.
Target: Financial Institutions, Stock Exchanges, and Healthcare Industry.
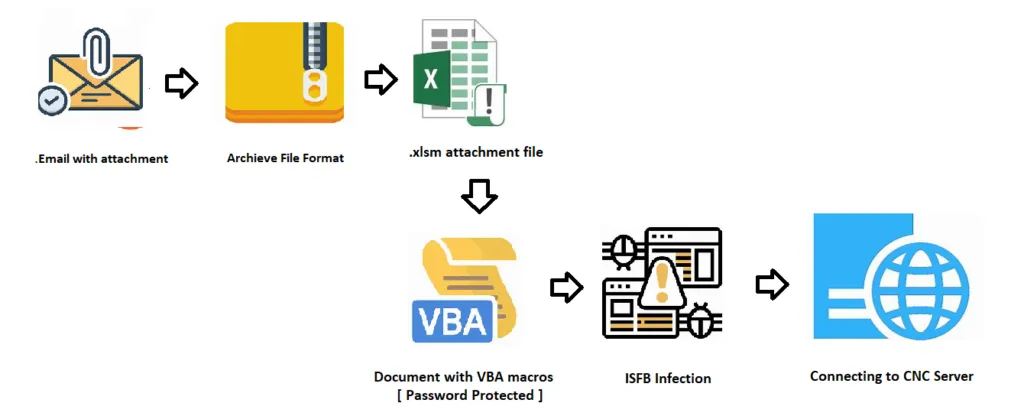
Infection Chain:

In our current example, ISFB threat actor attacks the victim machine by initial infection vector of spam campaign with attachment (EML). It contains a Microsoft Office document (MS Excel) document with VBA macro enabled content. The threat actor has tricks the user to enable the macros to perform their action. Once the user enables the content, the malware will connect with its C2 server to perform the defined actions for an objective.
Sample Information
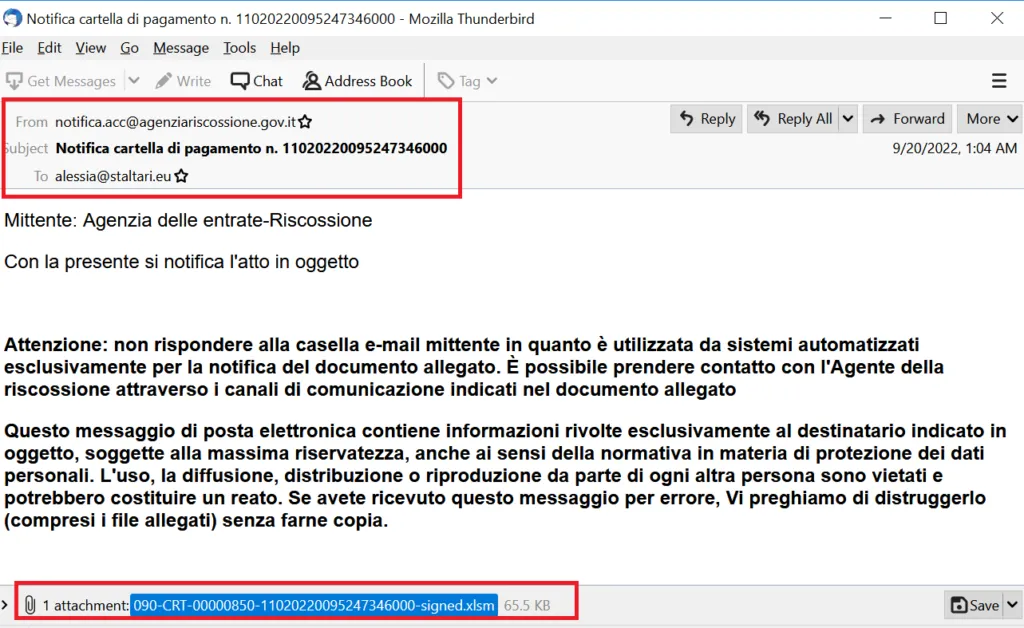
Phishing Email Contents
Sample 1: Campaign: ISFB or Gozi | Category: Banking Trojan
This time, the malware author sent many EML phishing content with same attachment file.
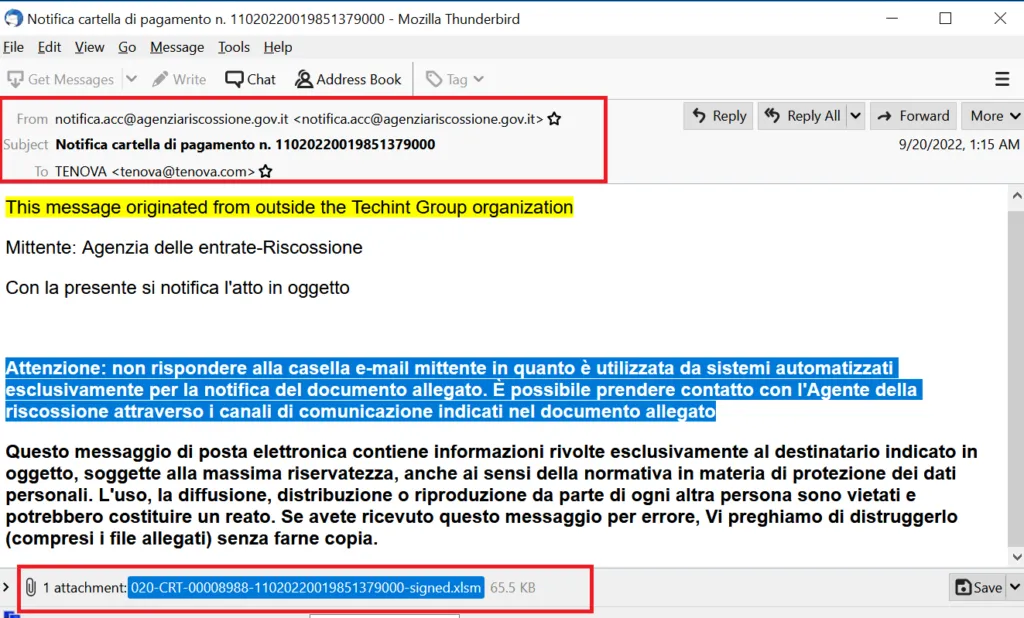
Sample 2:
Technical Analysis of XLSM attachment:
XLSM: b527de9bd7fb3abab3fc4b0cd95c46ebe2524b660cb6a970042272ae07a2689e
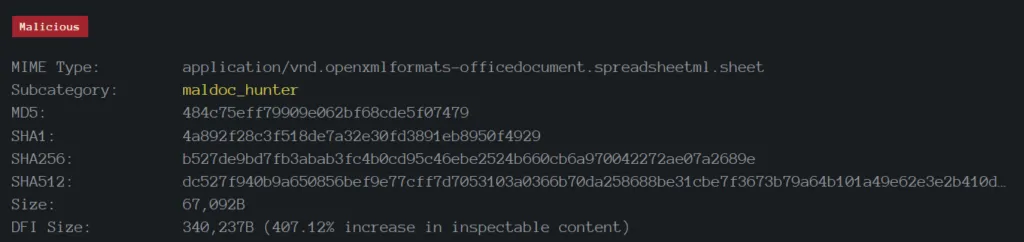
File Metadata / Properties:
Why are malware authors still using .XLSM infection?
XLSM files are spreadsheet files that support macros. A macro is a set of instructions that performs a record of steps repeatedly. XLSM files are based upon Open XLM formats that were introduced in Microsoft Office 2007. The malware authors are inserting the malicious VBA macros in the e-mail attachment files. Most of the time, macros will be in protected mode preventing regular users from viewing the code in clear text. In this sample as well, the VBA macro codes are protected mode with passcodes.
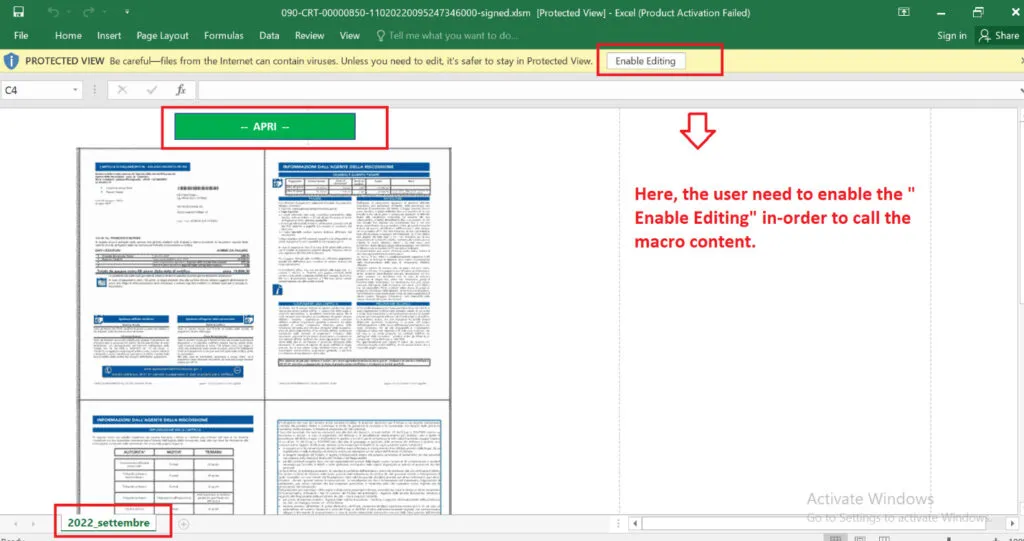
Enable-Editing:
Enabled Content:
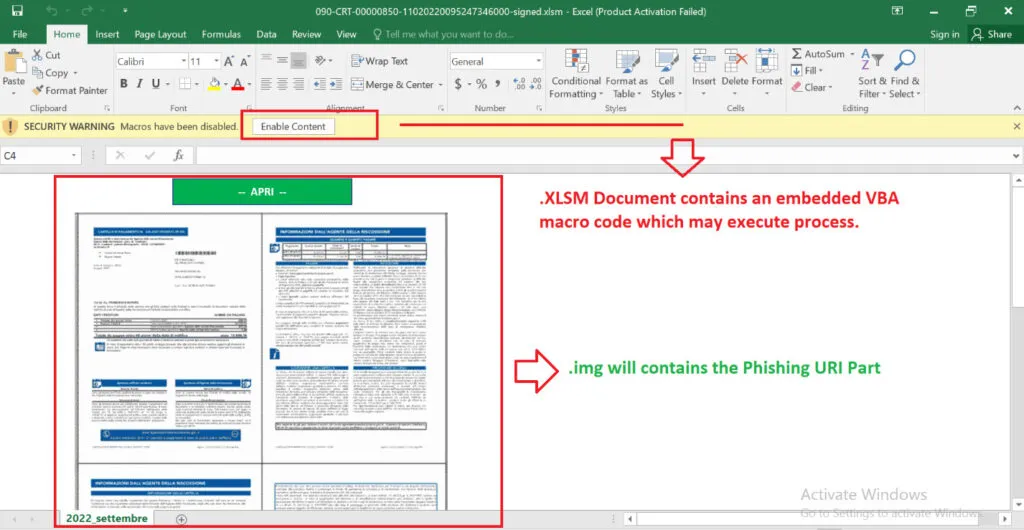
Once executed, the following actions will be performed by Gozi / URSnif malware;
- Once the user opens the attached document and enables a malicious macro which will trigger the download of a dynamic link library from a remote server.
- The downloaded .DLL file will be executed via RegSvr32.exe and unpack the core Gozi loader into memory, which is designed to manage all the interactions with the infected machine. (For Example: It checks the download/launch additional modules, and system update configuration)
- Gozi uses Internet Explorer (IE) COM objects to communicate with its C&C server and it creates a running instance through the CoCreateInstance() API.
- Mainly it checks for the few conditions to satisfy:
(a) The IP address must be located in Italy; and not be blacklisted (geofencing),
(b) The DLL must not have already been downloaded to create new infection.
Based on the sample observed, we found the following API calls,
Windows native API calls that give us an idea of the malware’s capability, described in the attack sequence,
• EnableMouseInPointer
• TrackMouseEvent
• GetsystemWindowsDirectory
• GetSystemAsFileTime
• GetVersion
• GetUILanguageInfo
• GetProcAddress
• CreateRemoteThread
• NtUserRemoteConnect
ISFB Trojan Attack Sequence:
1. Arrives as an office document attachment
2. User tricked into opening document and executed malicious macro
3. Users download malicious DLL
4. Malicious DLL is executed
5. Malware steals user data and credentials from browser
6. Victim‘s computer connects to the remote C2 server
7. Remote C2 server is executing backdoor commands on the victim’s computer
Initial – Indicator of Compromise [IOC]:
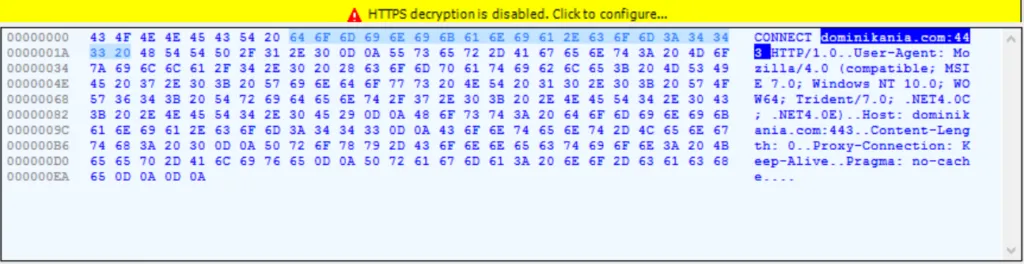
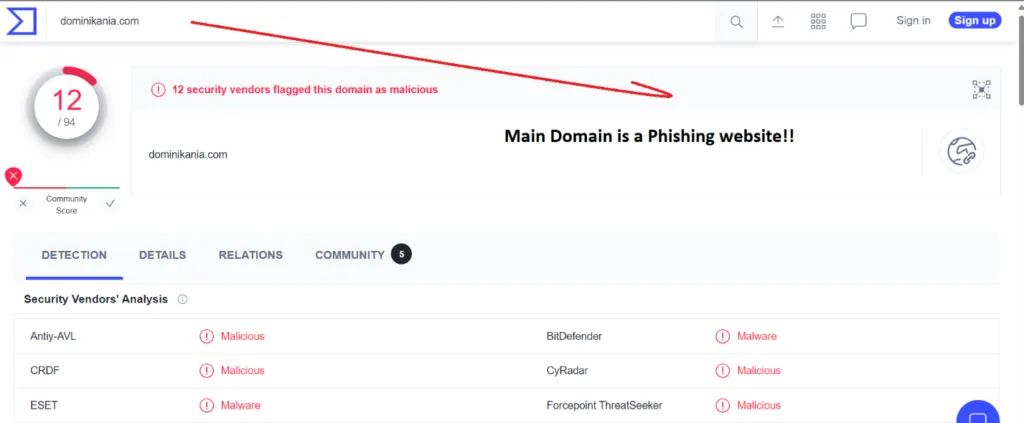
Virus Total Results:
Functionalities of ISFB:
- In general, it will be acting as info-stealer by collecting system activities and data (including network and browser data).
- Recording keystrokes (keylogging).
- Recording the videos or else making screenshots.
- Performing Man-in-the-browser [MiTB] attacks on the targeted websites. Usually, it’s used to intercept and/or modify data as it is being sent between a browser and a web server. (e.g., Form-grabbing, Web-injects).
- Redirect browser navigation to malicious websites.
- Enabling hVNC (hidden-VNC) and SOCKS proxy.
IOC – Indicators of Compromise for detecting ISFB / GOZI / URSNIF
Hashes
1056EA3DAD265DD554362BC0BD67F08FA2B9F3E5839E6E4FB197831A15C8ACEF
C0E28D4E88C59688657C839C344E6C1289002EF0BA461EBBF3CD4B75949312E9
5A8F5497F864BEAC188B72F77B22E1CBC1ECBB476E53C14403BD5A69515A2670
EB0A49F46CB50FED3FF0C1EA5062F94E6BAAF367775500AF122CD48AA7B4C1EA
06463378AE58AC721A6129CA3E85E743CD65ADB9E636ED95FB2C3215C2C9C754
3087A86F6A90A4F8F485023CB848815BA473E607CCB96B180839CDDE847566D8
ED0C5F836B3B54EEFAFCB1CC05571C27D294C50FBA036E50E030A5189735F6DD
9F3AFEF4B3A589C4685F39D887725A664EC0FE78091069550402365E589F9D22
E61BEE46B1B943412D7C2342EA1FA52635606105A8EC4F2341AE66ACC2121671
74F057A1B3EBD62B8A352F709716C4EAC4DF8503A3D7AACE8F46EA6AA998B02B
2231EA447F6F794FAE6A54479627112EBBA77DD276402F628FBE8B2BA4EC372F
53619FE192047617262D8BFD02DF432156AD01896129785240E20339A0FBCD7A
EEC4B7ACBF2659D738179784ABEE9009268AB135B90A19EC326CA3D4359DD014
E673EED04BF609E9FE34D7129DB5F8DF5FAF941CC741C9FBCDA12DF828DCAEB0
BD9EB71BAA0D28BFF80CBFA742346AA8F6D08AC463CE85BD97B9842AA6A2BBCB
A650279899A57CBF1E21D1E481BB02E10715DF746F987999A67253AE8390C4D5
B1DFE684B1F75E3B5AE544C82BAA9183A1F7E886CF68FF16D21FD030482AF1A2
DE51BAE08FD7318C988EF54511B5C08D8C3D9BBB2FC03D76D97116A79AFB9E81
104E6094EF239AAE7E4317433E868B67108B8157627DC222F996CB087795334F
IP Address
172(.)67(.)149(.)13
93(.)94(.)199(.)139
62(.)173(.)154(.)224
190(.)147(.)189(.)122
141(.)8(.)193(.)236
5(.)62(.)38(.)208
54(.)177(.)212(.)176
54(.)38(.)220(.)85
64(.)70(.)19(.)203
5(.)79(.)79(.)212
84(.)200(.)110(.)123
141(.)94(.)176(.)124
51(.)89(.)115(.)213
185(.)53(.)178(.)7
185(.)240(.)103(.)83
217(.)12(.)199(.)168
31(.)41(.)44(.)27
162(.)255(.)119(.)93
192(.)64(.)119(.)244
178(.)210(.)89(.)119
Domains
avkit(.)org
rgyui(.)top
missrevolt(.)top
dominikania(.)com
citisec-online(.)co
simple(.)oceanwp(.)org
apkfab(.)com
js(.)boardurl(.)de
s(.)0cf(.)io
mtmx(.)jp
lh3(.)androidcontents(.)com
americafirstcommittee(.)org
filecr(.)com
cdn-redirector(.)glopal(.)com
profeducations(.)com
html(.)design
www(.)ekko-wp(.)com
presets(.)kingcomposer(.)com
autroliner(.)com
track(.)gowithads(.)com
ws(.)fakemailgenerator(.)com
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping to ISFB / URSNIF Threat
| Domain | ID | Name | Use | |
| Enterprise | T1071 | 0.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | Ursnif has used HTTPS for C2. |
| Enterprise | T1547 | 0.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | Ursnif has used Registry Run keys to establish automatic execution at system startup. |
| Enterprise | T1185 | Browser Session Hijacking | Ursnif has injected HTML codes into banking sites to steal sensitive online banking information (ex: usernames and passwords). | |
| Enterprise | T1059 | 0.001 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell | Ursnif droppers have used PowerShell in download cradles to download and execute the malware’s full executable payload. |
| 0.005 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: Visual Basic | Ursnif droppers have used VBA macros to download and execute the malware’s full executable payload. | ||
| Enterprise | T1543 | 0.003 | Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service | Ursnif has registered itself as a system service in the Registry for automatic execution at system startup. |
| Enterprise | T1132 | Data Encoding | Ursnif has used encoded data in HTTP URLs for C2. | |
| Enterprise | T1005 | Data from Local System | Ursnif has collected files from victim machines, including certificates and cookies. | |
| Enterprise | T1074 | 0.001 | Data Staged: Local Data Staging | Ursnif has used tmp files to stage gathered information. |
| Enterprise | T1140 | Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information | Ursnif has used crypto key information stored in the Registry to decrypt Tor clients dropped to disk. | |
| Enterprise | T1568 | 0.002 | Dynamic Resolution: Domain Generation Algorithms | Ursnif has used a DGA to generate domain names for C2. |
| Enterprise | T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | Ursnif has used HTTP POSTs to exfil gathered information. | |
| Enterprise | T1564 | 0.003 | Hide Artifacts: Hidden Window | Ursnif droppers have used COM properties to execute malware in hidden windows. |
| Enterprise | T1070 | 0.004 | Indicator Removal on Host: File Deletion | Ursnif has deleted data staged in tmp files after exfiltration. |
| Enterprise | T1105 | Ingress Tool Transfer | Ursnif has dropped payload and configuration files to disk. Ursnif has also been used to download and execute additional payloads. | |
| Enterprise | T1056 | 0.004 | Input Capture: Credential API Hooking | Ursnif has hooked APIs to perform a wide variety of information theft, such as monitoring traffic from browsers. |
| Enterprise | T1559 | 0.001 | Inter-Process Communication: Component Object Model | Ursnif droppers have used COM objects to execute the malware’s full executable payload. |
| Enterprise | T1036 | 0.005 | Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name or Location | Ursnif has used strings from legitimate system files and existing folders for its file, folder, and Registry entry names. |
| Enterprise | T1112 | Modify Registry | Ursnif has used Registry modifications as part of its installation routine. | |
| Enterprise | T1106 | Native API | Ursnif has used CreateProcessW to create child processes. | |
| Enterprise | T1027 | Obfuscated Files (OR) Information | Ursnif has used an XOR-based algorithm to encrypt Tor clients dropped to disk.[2] Ursnif droppers have also been delivered as password-protected zip files that execute base64 encoded PowerShell commands. | |
| Enterprise | T1057 | Process Discovery | Ursnif has gathered information about running processes. | |
| Enterprise | T1055 | 0.005 | Process Injection: Thread Local Storage | Ursnif has injected code into target processes via thread local storage callbacks. |
| 0.012 | Process Injection: Process Hollowing | Ursnif has used process hollowing to inject into child processes. | ||
| Enterprise | T1090 | Proxy | Ursnif has used a peer-to-peer (P2P) network for C2. | |
| 0.003 | Multi-hop Proxy | Ursnif has used Tor for C2. | ||
| Enterprise | T1012 | Query Registry | Ursnif has used Reg to query the Registry for installed programs. | |
| Enterprise | T1091 | Replication Through Removable Media | Ursnif has copied itself to and infected removable drives for propagation. | |
| Enterprise | T1113 | Screen Capture | Ursnif has used hooked APIs to take screenshots. | |
| Enterprise | T1082 | System Information Discovery | Ursnif has used Systeminfo to gather system information. | |
| Enterprise | T1007 | System Service Discovery | Ursnif has gathered information about running services. | |
| Enterprise | T1080 | Taint Shared Content | Ursnif has copied itself to and infected files in network drives for propagation. | |
| Enterprise | T1497 | 0.003 | Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: Time Based Evasion | Ursnif has used a 30 minute delay after execution to evade sandbox monitoring tools. |
| Enterprise | T1047 | Windows Management Instrumentation | Ursnif droppers have used WMI classes to execute PowerShell commands. |


