
At LMNTRIX Labs, we’ve accessed a malware sample exploiting the recently-discovered Microsoft Equation Editor buffer overflow vulnerability. The vulnerability, CVE-2017-11882, was patched in last month’s Patch Tuesday release, so if you haven’t already done so, you can install the patch here.
The flaw is a remote code execution vulnerability which allows attackers to run malicious code on a victim computer. It is present in all Windows versions released in the past 17 years. To be clear, this isn’t just a theoretical vulnerability – there is even evidence suggesting it is being exploited by the Iranian group APT34.
So, let’s take a look at the sample we’ve managed to get our hands on:
Sample Details:
| Filename | PO_GFC-17120001.doc |
| Md5 | a3d89108e4a13900c299d7c5f6d687e0 |
Exploitation Technique:
Over 17 years ago, Microsoft complied a component called Microsoft Equation Editor as part of Microsoft Office. The vulnerability exists because Microsoft’s out of process COM server is hosted by eqnedt32.exe running as a singleton process which can accept commands from foreign processes.
Our sample exploits the remote code execution capabilities of “eqnedt32.exe” and the OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) equation object flaw, which allows documents and other objects to be embedded or linked to in applications.
Distributed via spam email, the malicious doc file “PO_GFC-17120001.doc” includes “OLEStartupAsServer” and “OleObjSetExtent called; x = %d, y = %d, EMBED Equation.3” which shows the sample is targeting the OLE flaw.
Process Diagram:

The malicious word file (PID:3024) spawns Equation Editor (PID: 3540) which calls the CMD.exe (PID:2168) to communicate with the Command and Control (C2) server hosted at 185[.]45[.]192[.]7.
The command issued from the C2 launches the payload to execute on the Windows Equation Editor.
At the time of analysis, not only is the C2 server still active, but no Antivirus vendors were able to detect the URL as malicious.
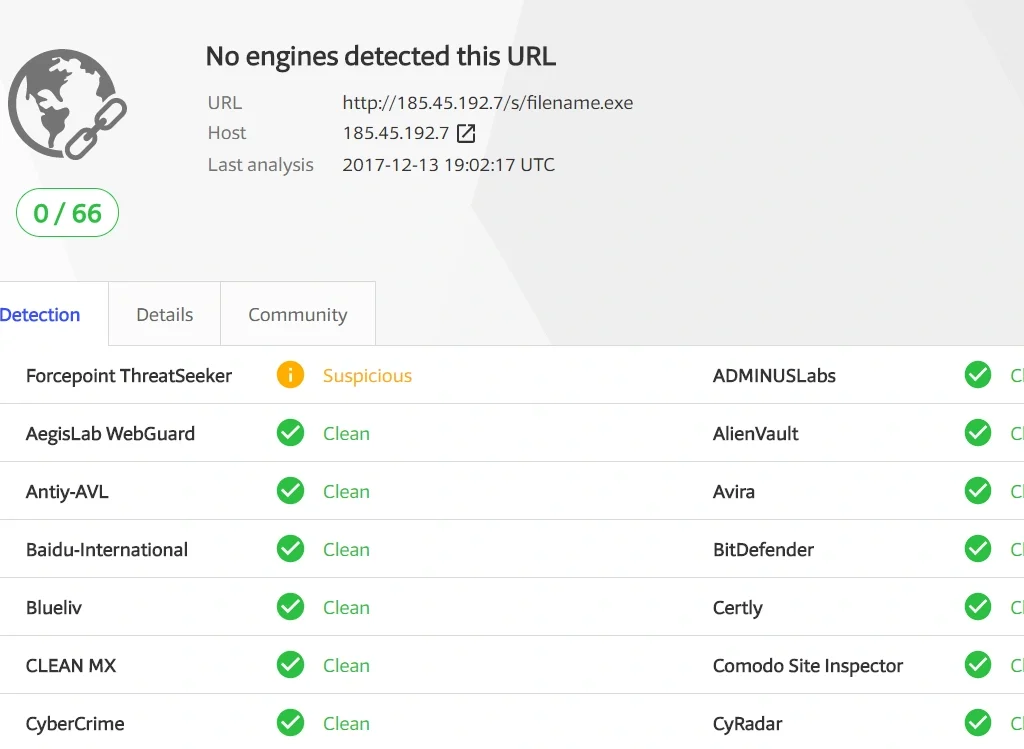
Once the malicious command from C2 is executed on the victim machine, the attackers take full control of the machine by running the exploit code.
IOC’s:
MD5: – a3d89108e4a13900c299d7c5f6d687e0
MD5: – 535899a1097b1105d2473637d4a86491396212e5
URL:
http[:]185.45.192.7\s\filename.exe
smb[:]//185.175.208.10/s/r.exe
smb[:]//185.175.208.10/s/p.exe
http[:]//78.46.152.143\\webdav
Mitigation:
Although mentioned in the introduction, if you haven’t applied Microsoft’s latest security patch, you can do so here. Seriously, do this now.
Alternatively, Equation Editor can also be disabled. This article shows step-by-step how to do so.


