
Consumers aren’t the only ones riding the iPhone8 hype wave, hackers are surfing it too. On the same day that Apple officially unveiled its latest release, LMNTRIX’s Cyber Defence Centre discovered an expertly crafted Apple-themed phishing campaign, we believe is designed to take advantage of the frenzy.
Cyber attackers were clearly prepared for the announcement, crafting an extremely sophisticated landing page, designed to trick users into submitting their details after receiving a spoofed ‘Apple Payment Confirmed’ email.
Below we see the initial email sent to users. Note the grammatical errors and spelling mistakes that typically signify a phishing campaign:
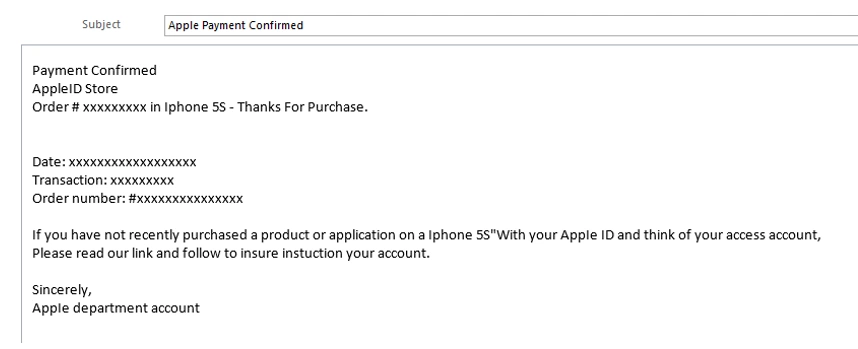
Figure 1. Initial Phishing Email.
A malicious PDF attachment was sent along with the email. A URL embedded in the attachment redirects users to the phishing page. This PDF is shown below:
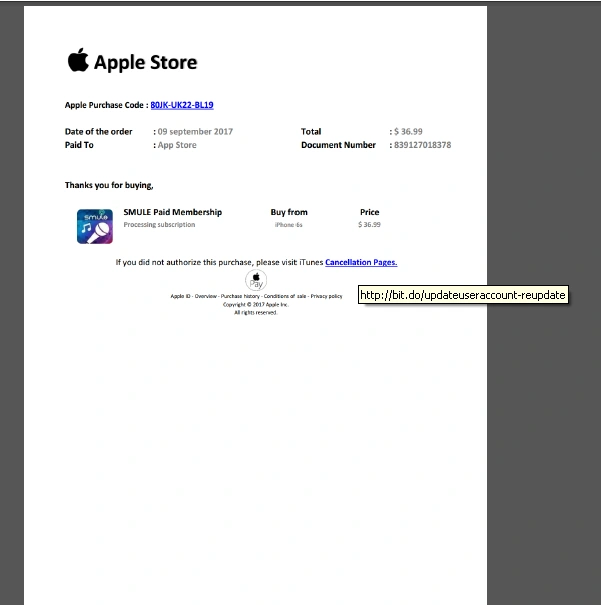
Figure 2. PDF Attachment with malicious cancellation link
Static analysis on the pdf file confirmed the following details:
| MD5 | 5a92d388ead084e794361eaba850fc6f |
| SHA-1 | ce823825fd764b0d3d7254bff0607c55de263bfc |
| File Type |
We quickly ruled out the possibility of malicious macros or other scripts. This campaign relies entirely upon a victim following the embedded URL:
| Type: /Action Referencing: << /Type /Action /S /URI /URI (http: / /bit.do /updateuseraccount-reupdate ) |
Above, we see the domain: hxxp://bit(.)do/updateuseraccount-reupdate
To further understand the hosting infrastructure, we executed the pdf in our controlled environment and observed its actions.
The initial email is designed to imitate that of a successful Apple purchase. In order to cancel the purchase, the user is asked to click the phishing link in the attachment. (See figure 2).
This pdf was crafted as a call to action. The timing of the campaign, together with the vague payment confirmation details in the initial email, lead us to suspect the campaign was deliberately timed with news of the iPhone 8 release. With Apple front of mind for many users, this would entice more victims to open the pdf.
Once opened, the pdf says a SMULE Paid Membership has been purchased. SMULE is a karaoke app. Along with the malicious link embedded in the cancellation code, the Apple purchase code also redirects to the same phishing page.
We then visited the phishing URL:
hxxps://secureid.sign-idapple.unathorized-purchase-au(.)com/

Figure 3 Safe Browsing
Below is the fake Apple page:
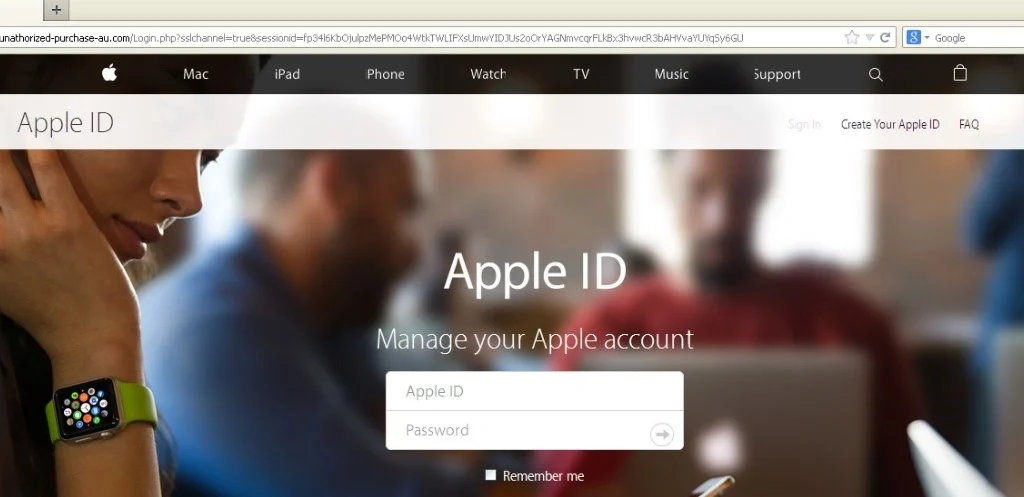
Figure 4 Fake Apple Page
The full domain is: hxxps://secureid.sign-idapple.unathorized-purchase-au(.)com/Login.php?sslchannel=true&sessionid=fp34l6KbOjulpzMePMOo4WtkTWLIFXsUmwYIDJUs2oOrYAGNmvcqrFLkBx3hvwcR3bAHVvaYUYqSy6GU
Given the highly sophisticated landing page, a victim could be forgiven for believing this was a legitimate Apple page.
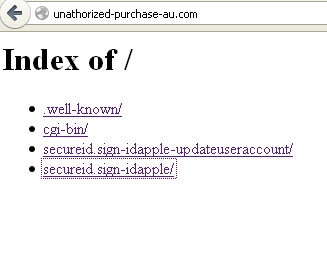
We then visited the parent domain and found the entire domain has been used for phishing purposes with fake pages.
Conclusion and mitigation
Given the hype surrounding all-things-Apple at the time of a new iPhone release, we believe this phishing campaign has been deliberately timed to take advantage of the increased interest.
Blocking the malicious URL will greatly help protect users against this campaign.
Traditional anti-virus programs won’t detect this sample automatically, the signature must be updated manually by blocking the malicious
IOC: URL: hxxps://secureid.sign-idapple.unathorized-purchase-au(.)com/.


