
This year’s relentless ransomware rampage continues to rage on – this time the culprit has been dubbed ‘BadRabbit’.
The variant has been spreading through Russia, Ukraine, and other Eastern European countries – specifically targeting corporate networks. So far, the computer systems for the Kiev Metro, Ukraine’s Odessa International Airport, several Russian media outlets, and others have been affected, with systems encrypted and a 0.5 bitcoin (about $280) ransom being demanded to restore file access.
Bad Rabbit has been initiated through drive-by downloads from a malicious PE file called “install_flash_player.exe”. Upon execution, the malicious file drops Mutex files which initiate the infection.
A drive-by download involves injecting Javascript into a website’s HTML body or a .js file. Then, when a victim visits a compromised site, a pop-up appears, saying Flash Player needs to be updated, essentially tricking users into installing the malware themselves.
Propagation – drive-by download:

The reason Bad Rabbit has been spreading like, well, rabbits, is because it uses the same leaked NSA exploit – EternalBlue – which helped WannaCry and Petya wreak havoc earlier this year.
EternalBlue is relatively easy to protect against. The exploit targets servers with SMB network sharing exposed to the Internet which is a feature that can (and should) be deactivated.
Static File Details:
From the Static File Details we can see the different file type names used in the campaign. The Copyright, Description, and Internal name section are spoofed to hide the malicious nature of the file:
Process Diagram:
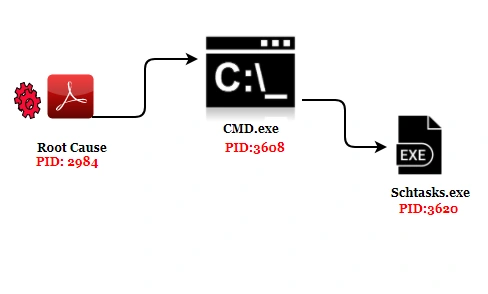
The root cause process is PID:2984 , which is called from cmd.exe (PID 3608) before process injection for schtasks.exe (PID 3620) kicks in which executes the ransomware:
Encryption File type:
.3ds.7z.accdb.ai.asm.asp.aspx.avhd.back.bak.bmp.brw.c.cab.cc.cer.cfg.conf.cpp.crt.cs.ctl.cxx.dbf.der.dib.disk.djvu.doc.docx.dwg.eml.fdb.gz.h.hdd.hpp.hxx.iso.java.jfif.jpe.jpeg.jpg.js.kdbx.key.mail.mdb.msg.nrg.odc.odf.odg.odi.odm.odp.ods.odt.ora.ost.ova.ovf.p12.p7b.p7c.pdf.pem.ppt.rtf.xls
IOC:
http:\/\/1dnscontrol[.]com/flash_install[.]php
Policy: C:\Windows\infpub.dat [Block File creation & execution]
Argumentiru[.]com
Fontanka[.]ru
Adblibri[.]ro
Spbvoditel[.]ru
Grupovo[.]bg
inematurk[.]com
http:\/\/185[.]149[.]120[.]3/scholargoogle/
MD5:
fbbdc39af1139aebba4da004475e8839
1d724f95c61f1055f0d02c2154bbccd3
b14d8faf7f0cbcfad051cefe5f39645f
Recommendations:
Key recommendations to mitigate against BadRabbit include:
• Disable WMI service (if it’s possible in your environment) to prevent the malware from spreading over your network.
• Disable SMB network sharing
• Patch the system from Vulnerability MS17-010.
• The Perimeter rule can be implemented on the Perimeter device (such as Proxy), to stop the download or communication of unauthorized Flash-player updates. See below:
| Title: Flash Player Update from Suspicious Location description: Detects a flashplayer update from an unofficial location logsource: category: proxy detection: selection: cs-uri-query: – ‘*/install_flash_player.exe’ – ‘*/flash_install.php*’ filter: cs-uri-query: ‘*.adobe.com/*’ condition: selection and not filter |
In addition, backing up files regularly ensures you can recover important data in the event you fall victim to any ransomware attack.


