QakBot (a.k.a QBot) is one of the leading banking trojans, it still continues to grow and develop, with more capabilities and new techniques. Its main purpose is to steal banking data (banking credentials, online banking session information, victim’s personal details, etc.). However, its developers have also developed functionalities that allow QBot to spread itself, evade detection and debugging, and install additional malware on compromised machines, such as Cobalt Strike, REvil, ProLock, Egregor and Black Basta ransomware.
Follina / Dogwalk Vulnerability Used to Deliver QakBot
Around November 2022, LMNTRIX spotted a pattern that showed a triple-threat attack on Microsoft Windows users. Threat actors are using phishing attacks to install Qakbot/Qbot malware “without” showing a Mark of the Web (MoTW) security warning to stop the attack. Several types of malware are being sent out using the recently discovered Windows flaw called Follina (Dogwalk) with CVE-2022-30190, which users still haven’t fully fixed.
Normally, when files are downloaded from untrusted sources such as suspicious, or malicious websites on the the Internet, for email attachments/downloaded files, Windows will add a special attribute called “Mark of the Web” to the file. This attribute is an alternative data stream that tells you where the file came from, who sent you there, and where you can download it. When a user tries to open a file with the MoTW attribute, Windows will show a security warning and ask the user to confirm that they want to scan the file / open the file directly.
In the same week, LMNTRIX CDC observed that a major cybercrime group with the identifier TA570 had used CVE-2022-30190 to send out Qbot, a widely used info-stealer also called Qakbot. Qakbot can spread on networks that have been hacked and several cybercrime groups have used it for getting initial access.
The Follina vulnerability has a large impact because it affects ALL Microsoft Office 2013 version and upwards – on ALL currently supported Microsoft Windows operating systems, including the most recent: Win 10, Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2022 also! Microsoft Office offers a very lucrative attack surface as, its the most popular productivity suite on the planet, with over a billion installation on computer devices.
Target Platform – Windows Users
Activity of the Qbot in the Wild
- Collecting information about the compromised host.
- Stealing credentials (from browser data and cookies).
- Targeting web banking links.
- Password brute-forcing.
- Registry manipulation and creating scheduled tasks (for persistence).
- Laterally moving through the network.
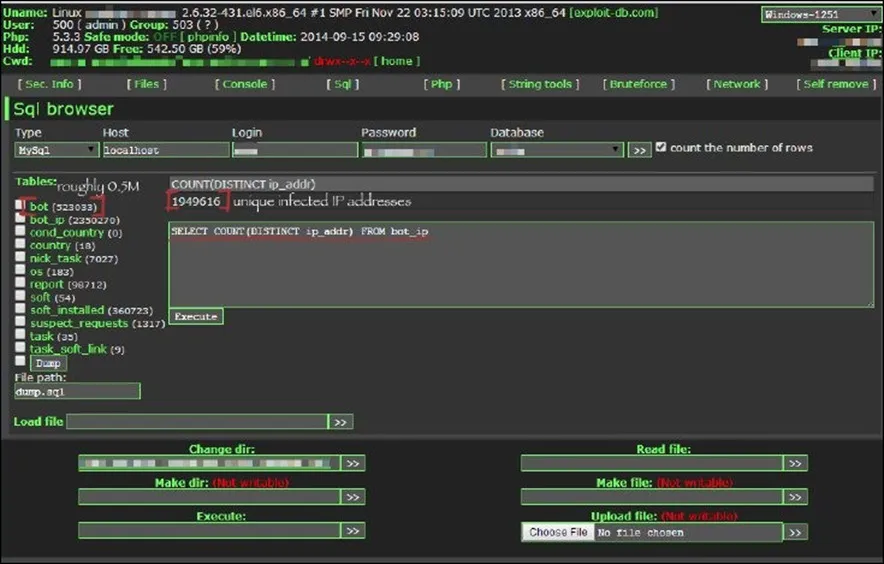
Infection Chain
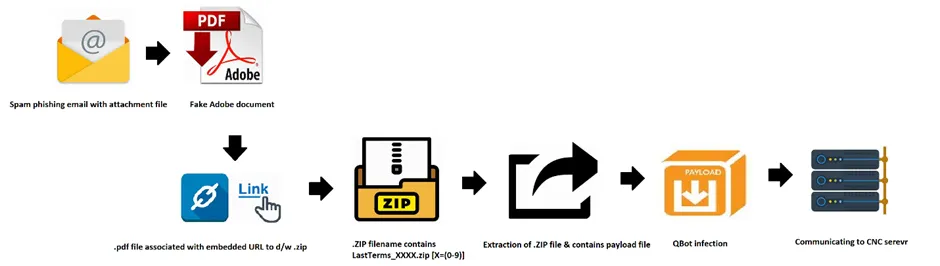
The new QakBot infections are done by the initial vectors such as .PDF documents. As usual this can be done by using phishing campaigns or, malspam emails. Once the victim opens the email attachment containing the .PDF document, then the .PDF file will communicate with the external link to download the ZIP file. The embedded .ZIP file will have the final payload file. Each time they will dynamically change their IOCs to avoid being detected by antivirus software.
QakBot Initial Infection (Loading Sequence)
During the summer months of June and July 2022, LMNTRIX NDR observed variations of the following pattern of network activity on several active client networks;
- HTTP Connection – The user’s device connects to an email service like Outlook.com or Google Mail.
- Stage 1 (Loader) – The device sends an initial HTTP GET request with an Office user-agent string and a ‘/123.RES’ target URI to C2 Server. The request is answered with a HTML file containing the exploit for the Follina vulnerability (CVE-2022-30190). This HTML file downloads a .zip file via HTML smuggling.
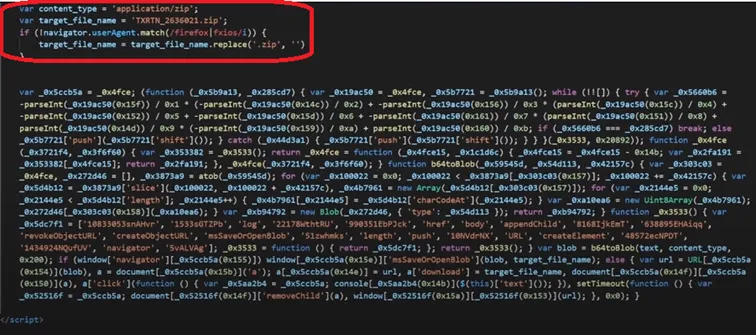
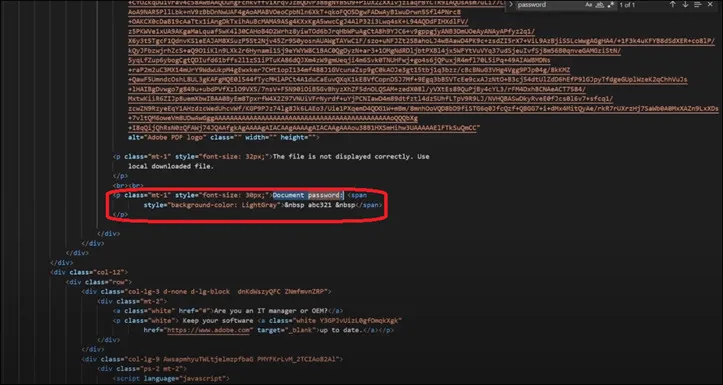
- Stage 2 – Now the device sends another HTTP GET request with cURL to a target URI that ends in “.dat” to an unusual external endpoint. The request is responded to with a Qakbot DLL sample (DLL sideloading method). This download.dat / downloads.dat is actually a zip file… When trying to extract the zip file, it requests for a password.
- Password: Upon closer static analysis the contents of the zip file are encoded with Base 64, when decrypting, we can use the password: “abc321” (without quotes)
• QakBot Malware uses a modified regsvr32 binary to execute its DLL payload.
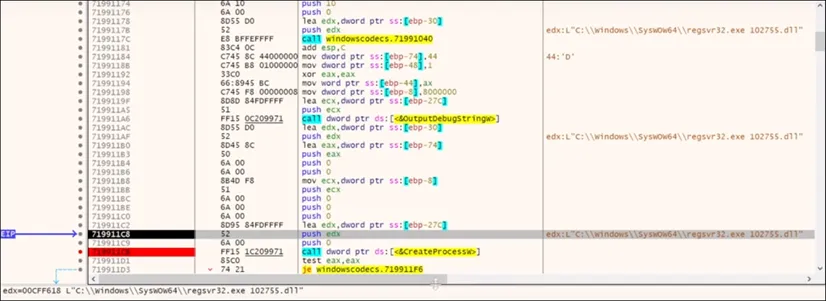
- C2 Access – Lastly the infected device goes ahead and connects to QakBot Command and Control servers over ports such as 443, 995, 2222, and 32101 to perform desired actions on objectives.
What is HTML Smuggling?
Most of the incidents observed by LMNTRIX involved Qakbot in June/July 2022. The machines were infected likely through HTML smuggling. HTML Smuggling is when malicious code (javascript shellcode, or just javascript) is put into HTML attachments to drop a secondary payload. Based on open source intelligence reports and patterns of network traffic observed, we believe the Qakbot infections seen across LMNTRIX client base in June 2022 started with one of the following three methods:
Option A – When the user opens an HTML attachment, a ZIP file is downloaded to their device. The ZIP file has a Qakbot DLL file and, an LNK shortcut file. When the LNK shortcut file is opened, the DLL file gets loaded for further malice.
Option B – When the user opens an HTML attachment, a ZIP file is downloaded to their device. ZIP file contains a docx file that, when opened, sends an HTTP GET request to C2 Server with an Office User Agent string and a ‘/123.RES’ target URI from the user’s device. If the HTTP GET request works, an HTML file with a Follina exploit is sent back as the response. The Follina exploit makes the user’s device send an HTTP GET request to an outside server with a.dat target URI. Subsequently a Qakbot DLL file is downloaded to answer the request.
Option C – When the user opens an HTML attachment, a ZIP file is downloaded to their device. ZIP file has an LNK file that, when opened, makes the user’s device send an initial HTTP GET request with a cURL string and a.dat target URI. If successful, the HTTP GET request downloads a Qakbot DLL.
Sample Information

Technical Analysis of PDF document
A PDF file is a multi-platform document created by Adobe Acrobat or another PDF application. The PDF format is commonly used for saving documents and publications in a standard format that can be viewed across multiple platforms. In many cases, PDF files are created from existing documents instead of being created from scratch. PDF file format has an important feature that allows the author/creator to add a hyperlink any URLs or any attachments to perform actions or, to ensure that your reader has immediate access to related information. This makes it conducive for malware authors to achieve their action on objectives.
Qbot – Fake Adobe Template
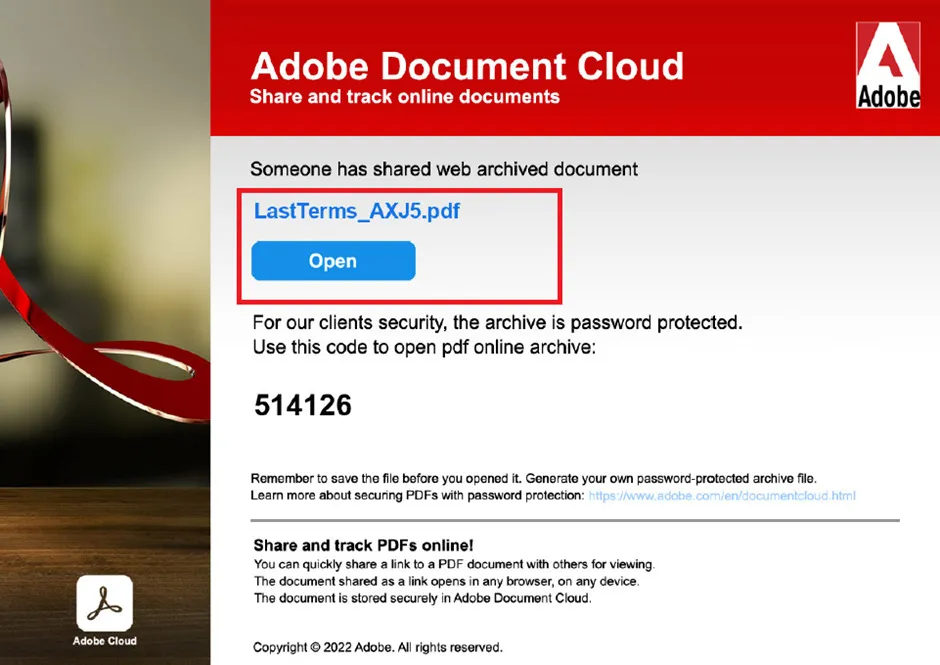
The above image shows the fake Adobe template which contains the XXXX.pdf file. In-order to open the .PDF, they have provided a password. After opening the pdf file by using SFX extraction, .ZIP file will drop the payload file and take further action. An SFX file is a compressed archive that has been combined with an executable module, allowing Windows users to extract the archives without a decompression program. It is typically saved with .EXE file extension, but may sometimes use the ‘.SFX’ extension also. When double-clicked in Windows, SFX files automatically decompress themselves and extract data that’s present inside the archive.
Embedded URL
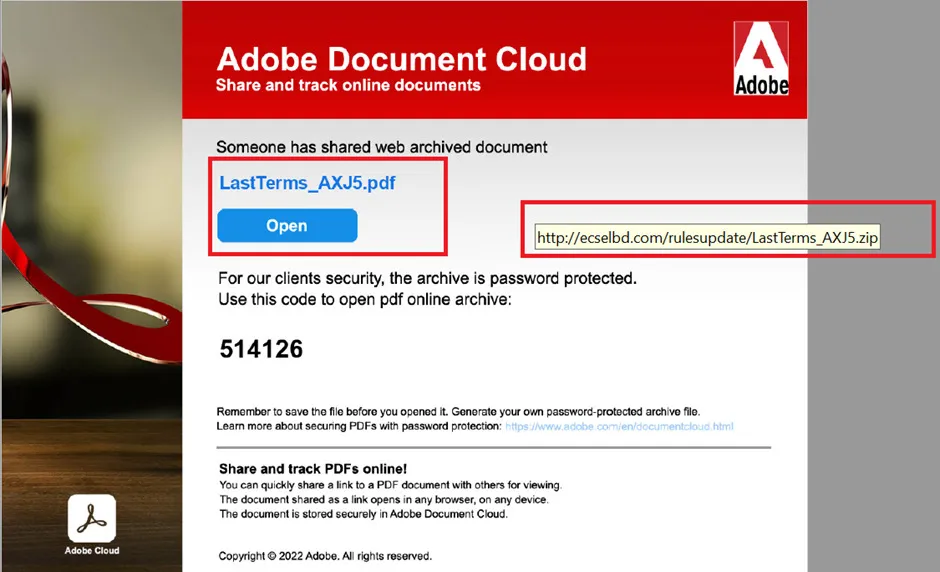
Here we can see the associated external URL & the password to open the .ZIP file.,
PDF designers and the PDF reader software architects never intended for files to be able to modify the operating system running the PDF reader. Malware authors have found ways to exploit PDF readers’ software vulnerabilities and have creatively used the PDF language, enabling them to produce PDF documents that execute arbitrary code.
PDF Contents
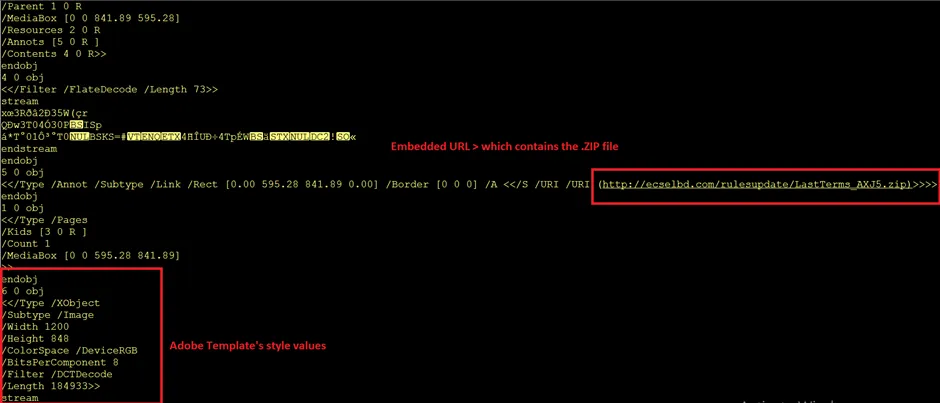
Embedded IOCs
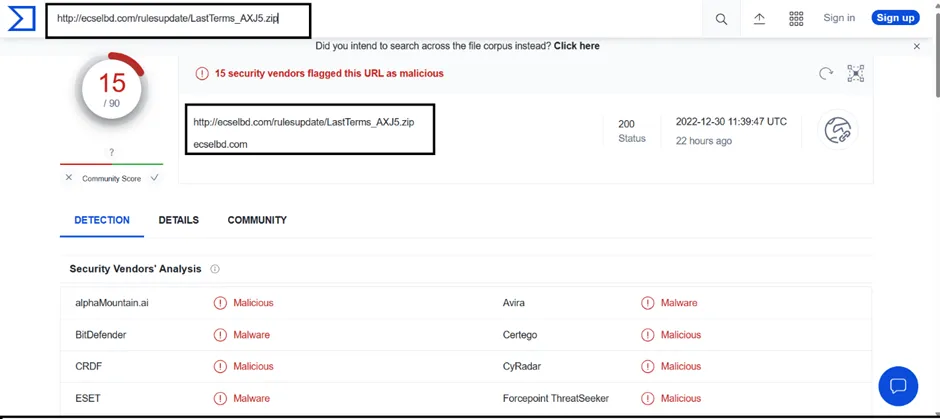
Most of the security vendors detect this URL as a Phishing/malicious site. Also, the status code is “still alive”.
Communicating & File Referring
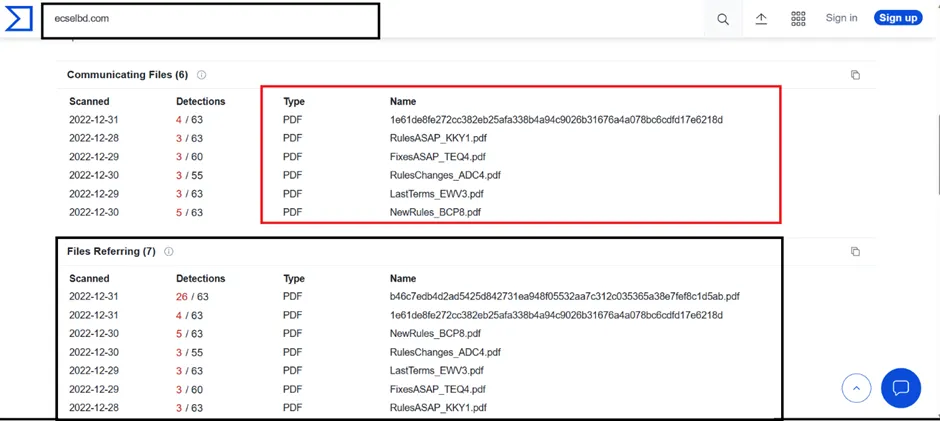
Still the QakBot sample communicates with the multiple domains to drop payloads on the victim’s machine.
Once the system is infected, it will do the following:
- Collect information about the compromised host. s
- Set up tasks to run at a certain time (privilege escalation & persistence).
- Gathering credentials. Dumping credentials (.exe access).
- Password stealing (from browser history and cookies).
- Targeting web banking links (web injects).
- Password brute-force attacks.
- Changes to the registry (persistence).
- Process injection is used to hide the malicious actions
– The malware gets deployed in stages, and it has built-in AV evasion techniques.
Indicators of Compromise (QakBot)
| SHA256 | MD5 |
| ba8b5bd13d0d0b1f36200113c4e48d02319953abb505542a7b91d5c3b09c57d8 | 103a105e14bccf015d7854fa2df11e07 |
| f38573d220f72973dbff6950841879b91e585991e13f31a99731893340aafb79 | 66a790c42af6e182d0a0cfc7d02e96b0 |
| 2b44638c6ad4b654b8d72e1c4297f96de5df45ff39c306c1331f7c26608b27d2 | bd286964d57d034a4356f50cd7ac2927 |
| 6bb35cbd8c3412d0e5846f53389d879b09fce0da5e058319b188bc175a55f508 | 3d0c5aef3dd4a7305fd55c26c46df91b |
| d532b4287d2f166b2e7245b25840c141b619f1bb09d076b3ecfd1c11c4af0527 | 912933691df22fe049fc2943c2b89df6 |
| 32a941abca850eade46198cee2f12475c05a0a712a61f11b91da289bf1decd26 | 959f79799ed2b8bbf6f0c909d7006991 |
| bc57404dd4f221835ffdeec579b9082977cac167c7e07d58479e1eb96a501f59 | 6ba112f8e8a16eba9f48283254201149 |
| b9efb8b9e271b08de4b59d78720796e7b428a989e8d7cb05f01713ea526b86dd | fdd112c79808f54c51315a2db79543a3 |
| 503e62505c8567bfdb66fcd1119b2a5769c3dd6b3748a3a4eb9aa9430b3a4a1c | 9ad36d75200197d301f224eacc3dd943 |
| 057c19f997063f7f280cc5b994811f66186254fb876a481dbf38e75d62396938 | e5ccc1392ba29b751bef1dffcee92ed4 |
| f88628c90409fbea143a7b84a6fd93b386751d3ccbff8be7d47fb0a1f344358e | 2cb93a0023d91646ce8d74e2f6f03384 |
| 3ef60c9eba24bad44365f16197186c2d50c60f8614321d558d3f7094612974a0 | 4cc0c0f76f10a174fa51ddc63806e246 |
| 3018f66ea99268cd99ea492c3a0dba9862942d65fce9b30c99eb4656c31f7730 | 302c7aa6136eea2ec5fdb22f81e60bb5 |
| c463739e8772972522efa041317e48c01058e25bab4fe905f9c36d37bc7e8e53 | 923e13203badd300944fa7129cbafcf5 |
| 24c17ce932f90c4384fb238f876506a5042d6d44854e37176be68e51b819669e | a491c72daca578ebf7a36e3c8efad536 |
| 23a18808569cbf6ab77553991ec60a0696652d2ceb3ce483d45419930081ee6e | 800ba8cba33c779b24600d1542885ef5 |
| b97c7807fba67a43610dea8320d1b33f0aa258eed46068cee49fd7b83172f10a | b6abedbc7579ac7f1eb2994a70b4bcab |
| de2517dfb2180d476bad32be431dbb3361a57439cd018f913533ce41a9a6c5db | b58be2871cac99cae177b4e6b665d27f |
| b77b642ecd371710a2725e6509cb0cc0a0c502504fcbac86cfdb7092659e5017 | 8cf7c5bf9ba9479682cea19a2ff3d6b2 |
| Malicious URL |
| hxxp://clipgroups(.)com/eimc/tuelasuedct |
| hxxps://ventokanta(.)com/te/ueqit |
| hxxps://hidrolatina(.)cl/nsi/dipmmieuteqcu |
| hxxps://karaoke(.)pk/ume/index(.)php |
| hxxps://osciloscopiopassoapasso(.)com/oeu/index(.)php?QBOT(.)zip |
| hxxp://gemsarchives(.)com/sa/olieodvlrt |
| hxxps://sportsdayonline(.)com/smna/index(.)php?qbot(.)zip |
| hxxps://vikominstitute(.)com/pau/aqaettuu |
| hxxps://seedbeej(.)pk/tin/index(.)php?QBOT(.)zip |
| hxxps://odix(.)in/iet/nempoaissniet |
| hxxps://dominosoft(.)ir/nusq/index(.)php?qbot(.)zip |
| hxxps://yawajobs(.)com/tc/leluaatnm |
| hxxps://saiyyedakhtaraligroup(.)com/tuol/index(.)php?qbot(.)zip |
| hxxps://silent-power(.)co/tiic/tesqiudme |
| hxxps://vakrangeedevelopers(.)com/amss/qakbot(.)zip |
| hxxps://pulseglobalservices(.)com/tro/C7MgkLHCvb(.)zip |
| hxxps://worldmaxtv(.)com/eies/iuqonn |
| hxxps://laxmeditech(.)com/tue/aduinilunntaicudmt |
| hxxps://clinicapalazzo(.)com/rem/contractAnne |
MITRE ATT&CK Tactics & Techniques for QakBot
| ID | Tactics | Techniques |
| TA0001 | Initial Access | T1566.001 – Spearphishing Attachment |
| TA0002 | Execution | T1027 – Obfuscated Files or Information T1059.005 – Visual Basic T1204.002 – Malicious File |
| TA0003 | Persistence | T1053.005 – Scheduled Task T1547.001 – Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| TA0004 | Privilege Escalation | T1053.005 – Scheduled Task |
| TA0005 | Defense Evasion | T1027.002 – Software Packing T1055 – Process Injection T1055.012 – Process Hollowing T1497.001 – System Checks |
| TA0006 | Credential Access | T1003 – OS Credential Dumping T1110.001 – Password Guessing T1555.003 – Credentials from Web Browsers |
| TA0007 | Discovery | T1016 – System Network Configuration Discovery |
| TA0011 | C&C Server | T1071.001 – Web Protocols T1090 – Proxy T1090.002 – External Proxy |


