

LMNTRIX researchers recently identified a day-old variant of the Hermes malware in the United States. North Korea is believed to have used the original Hermes malware to target computers in South Korea, but the latest version has been found in the United States, which raises questions about whether the US may now be the new target. We should point out researchers are still uncertain about North Korea’s hand in the new variant and acknowledge that the targets could also be generally more global.
In at least one reported incident last year, an older version of the Hermes ransomware was used to hide money from a bank heist in Taiwan. Officials from Taiwan’s Far East International Bank (FEIB) were thwarted by encrypted data after successfully detecting irregular transactions. It is believed that the Lazarus gang allegedly responsible for the hack used Hermes to destroy and encrypt evidence of the breach and subsequent theft.
An interesting side note is the fact that South Korean security researchers at the Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) discovered a Flash Player vulnerability (0-day: CVE-2018-4878) in February 2018 that served as a distribution channel for MS Office files containing malicious Flash content. Exploit kit authors will likely be investigating this in depth considering that it is an ideal delivery method for Hermes 2.1 once it has been packaged as a drive-by download.
How Hermes 2.1 Ransomware Works
The team first collected available malware samples and did an initial analysis:
File Hash (SHA-256): 67f87032b561e99e9da0a768e2c6ce960123b2835266068dce1ece625e660d84
File Size: 327 KB
File creation- TimeDateStamp: (18th April 2018 – 14:18:59)
Infection
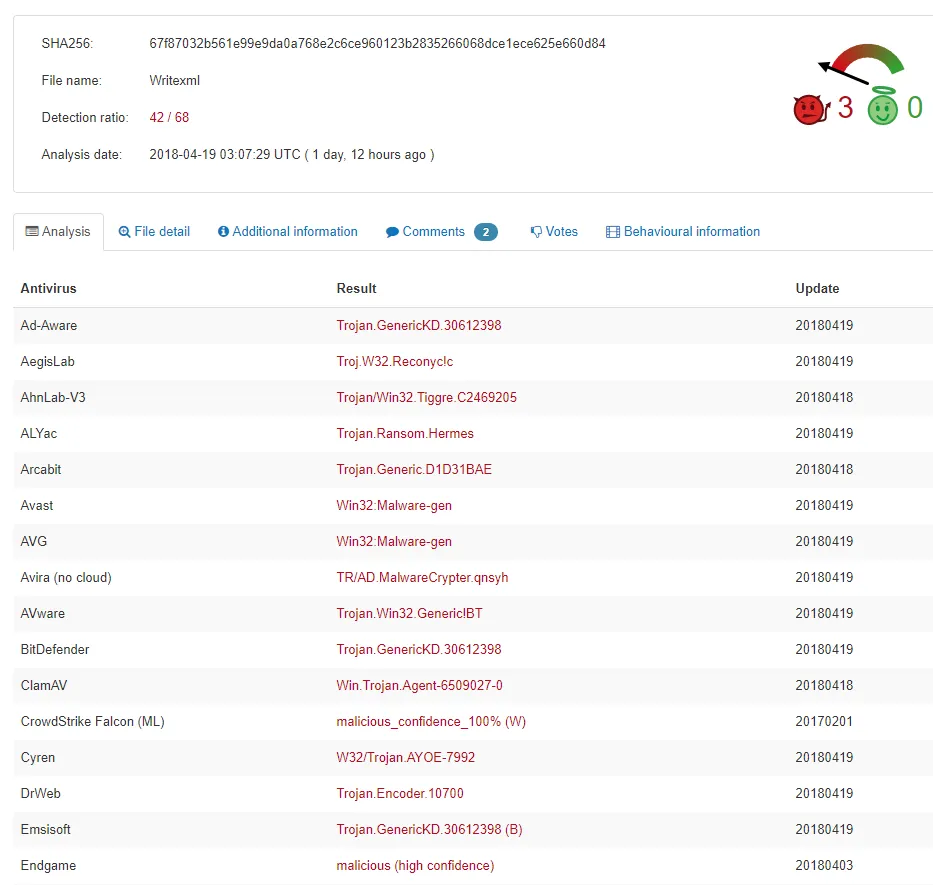
Figure 1: VT result for Hermes Ransomware
Analysis of the Ransomware sample
The team then checked the file’s PE details:
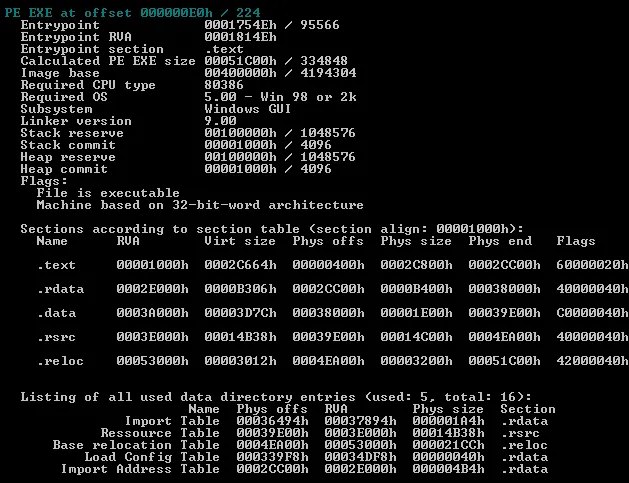
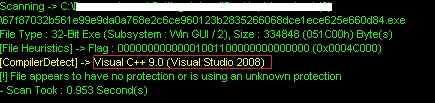
Figure 2: EXE File Type and compiled using VC++
When the team dissected the original sample, it led to interesting artifacts such as SetSecurityDescriptorDacl, a new file creation – probably a duplicate file of the original sample.

Figure 3: SetSecurityDescriptorDacl
This function is called for in order to set information in the discretionary access control list, acronymized to DACL. The use of DACL by attackers was discussed at last year’s BlackHat Conference. The screenshot below is an excerpt:

Figure 4: Description from BlackHat conference on DACL used by attackers
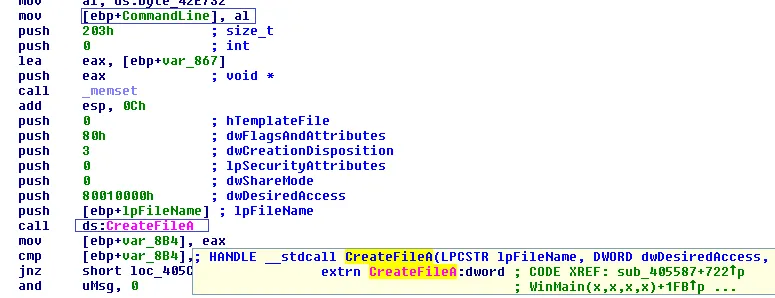
Figure 5: New File Creation
It creates a file in the %appdata% location, and we manually checked the hash of the file, which is actually a same hash of the original file. The file name is not random, and it is constantly creating the name ‘svchosta.exe’.
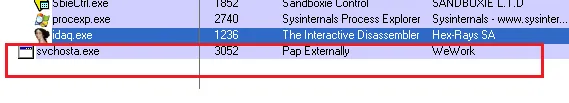
Figure 6: Spotted the svchosta.exe in running process
In the %appdata% location, we also spotted the decryption information html; i.e., the ransom note.
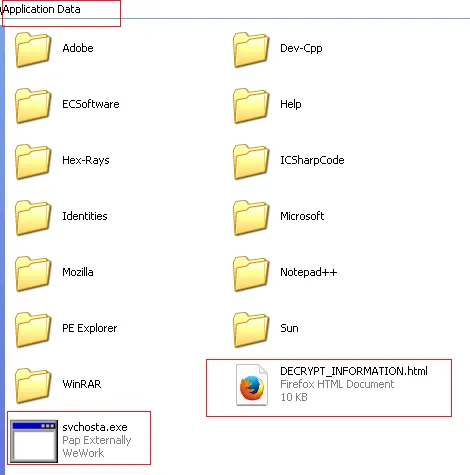
Figure 7: Malicious file in %appdata%
ENCRYPTION
On infection, the malware encrypted very important files on the desktop and My Documents, and dropped the decryption information html file. All the encrypted files had the extension .HRM.

Figure 8: Hermes Extension (.HRM) added after encryption

Figure 9: Ransom note and payment methods
Threat Indicator
IOC details
File hashes:
SHA 256: 67f87032b561e99e9da0a768e2c6ce960123b2835266068dce1ece625e660d84
File extension added by this variant of ransomware: ‘.HRM’
File extensions targeted:
| tif php 1cd 7z cd 1cd dbf ai arw txt doc docm docx zip rar xlsx xls xlsb xlsm jpg jpe jpeg bmp db eql sql adp mdf frm mdb odb odm odp ods dbc frx db2 dbs pds pdt pdf dt cf cfu mxl epf kdbx erf vrp grs geo st pff mft efd 3dm 3ds rib ma max lwo lws m3d mb obj x x3d c4d fbx dgn dwg 4db 4dl 4mp abs adn a3d aft ahd alf ask awdb azz bdb bib bnd bok btr bak cdb ckp clkw cma crd dad daf db3 dbk dbt dbv dbx dcb dct dcx ddl df1 dmo dnc dp1 dqy dsk dsn dta dtsx dxl eco ecx edb emd fcd fic fid fil fm5 fol fp3 fp4 fp5 fp7 fpt fzb fzv gdb gwi hdb his ib idc ihx itdb itw jtx kdb lgc maq mdn mdt mrg mud mwb s3m myd ndf ns2 ns3 ns4 nsf nv2 nyf oce oqy ora orx owc owg oyx p96 p97 pan pdb pdm phm pnz pth pwa qpx qry qvd rctd rdb rpd rsd sbf sdb sdf spq sqb stp str tcx tdt te tmd trm udb usr v12 vdb vpd wdb wmdb xdb xld xlgc zdb zdc cdr cdr3 ppt pptx abw act aim ans apt asc ase aty awp awt aww bad bbs bdp bdr bean bna boc btd cnm crwl cyi dca dgs diz dne docz dot dotm dotx dsv dvi dx eio eit emlx epp err etf etx euc faq fb2 fbl fcf fdf fdr fds fdt fdx fdxt fes fft flr fodt gtp frt fwdn fxc gdoc gio gpn gsd gthr gv hbk hht hs htc hwp hz idx iil ipf jis joe jp1 jrtf kes klg knt kon kwd lbt lis lit lnt lp2 lrc lst ltr ltx lue luf lwp lyt lyx man map mbox me mell min mnt msg mwp nfo njx now nzb ocr odo odt ofl oft ort ott p7s pfs pfx pjt prt psw pu pvj pvm pwi pwr qdl rad rft ris rng rpt rst rt rtd rtf rtx run rzk rzn saf sam scc scm sct scw sdm sdoc sdw sgm sig sla sls smf sms ssa stw sty sub sxg sxw tab tdf tex text thp tlb tm tmv tmx tpc tvj u3d u3i unx uof uot upd utf8 utxt vct vnt vw wbk wcf wgz wn wp wp4 wp5 wp6 wp7 wpa wpd wpl wps wpt wpw wri wsc wsd wsh wtx xdl xlf xps xwp xy3 xyp xyw ybk yml zabw zw abm afx agif agp aic albm apd apm apng aps apx art asw bay bm2 bmx brk brn brt bss bti c4 cal cals can cd5 cdc cdg cimg cin cit colz cpc cpd cpg cps cpx cr2 ct dc2 dcr dds dgt dib djv djvu dm3 dmi vue dpx wire drz dt2 dtw dvl ecw eip exr fal fax fpos fpx g3 gcdp gfb gfie ggr gif gih gim spr scad gpd gro grob hdp hdr hpi i3d icn icon icpr iiq info ipx itc2 iwi j j2c j2k jas jb2 jbig jbmp jbr jfif jia jng jp2 jpg2 jps jpx jtf jwl jxr kdc kdi kdk kic kpg lbm ljp mac mbm mef mnr mos mpf mpo mrxs myl ncr nct nlm nrw oc3 oc4 oc5 oci omf oplc af2 af3 asy cdmm cdmt cdmz cdt cgm cmx cnv csy cv5 cvg cvi cvs cvx cwt cxf dcs ded dhs dpp drw dxb dxf egc emf ep eps epsf fh10 fh11 fh3 fh4 fh5 fh6 fh7 fh8 fif fig fmv ft10 ft11 ft7 ft8 ft9 ftn fxg gem glox hpg hpgl hpl idea igt igx imd ink lmk mgcb mgmf mgmt mt9 mgmx mgtx mmat mat otg ovp ovr pcs pfv pl plt vrml pobj psid rdl scv sk1 sk2 ssk stn svf svgz sxd tlc tne ufr vbr vec vml vsd vsdm vsdx vstm stm vstx wpg vsm xar yal orf ota oti ozb ozj ozt pal pano pap pbm pc1 pc2 pc3 pcd pdd pe4 pef pfi pgf pgm pi1 pi2 pi3 pic pict pix pjpg pm pmg pni pnm pntg pop pp4 pp5 ppm prw psdx pse psp ptg ptx pvr px pxr pz3 pza pzp pzs z3d qmg ras rcu rgb rgf ric riff rix rle rli rpf rri rs rsb rsr rw2 rwl s2mv sci sep sfc sfw skm sld sob spa spe sph spj spp sr2 srw ste sumo sva save ssfn t2b tb0 tbn tfc tg4 thm tjp tm2 tn tpi ufo uga vda vff vpe vst wb1 wbc wbd wbm wbmp wbz wdp webp wpb wpe wvl x3f y ysp zif cdr4 cdr6 cdrw ddoc css pptm raw cpt pcx pdn png psd tga tiff tif xpm ps sai wmf ani flc fb3 fli mng smil svg mobi swf html csv xhtm dat |
Mitigating the Hermes 2.1 Ransomware Threat
LMNTRIX recommends that users upgrade their Flash Player versions with the latest patch, as well as update their anti-malware applications with the latest malware signatures.
Although the original attack targeted South Korea, this particular variant is believed to be targeted at users in the United States. Researchers at LMNTRIX also suspect that the Hermes 2.1 Ransomware may also infect computers in other countries that are not the primary target.
We will update this research as new facts become available.
On 2018-05-14


