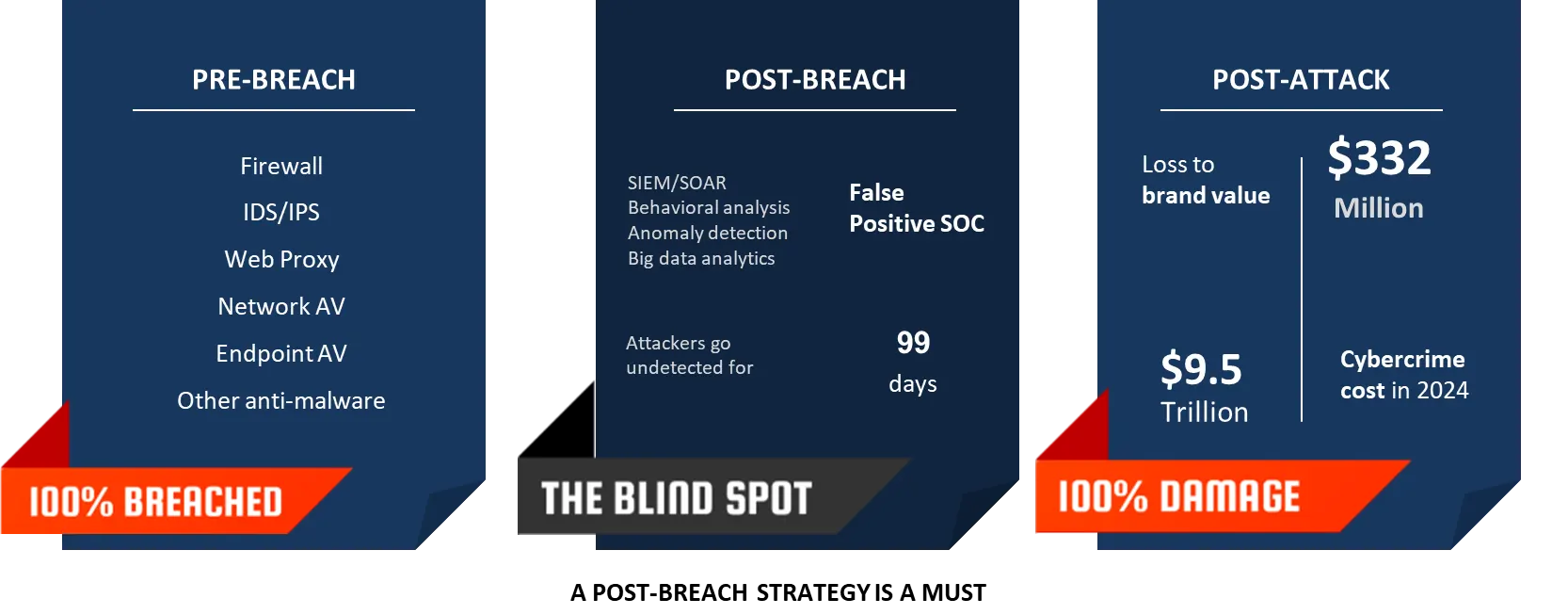
LMNTRIX Deceive
Unmask Attackers Before They Do Real Damage
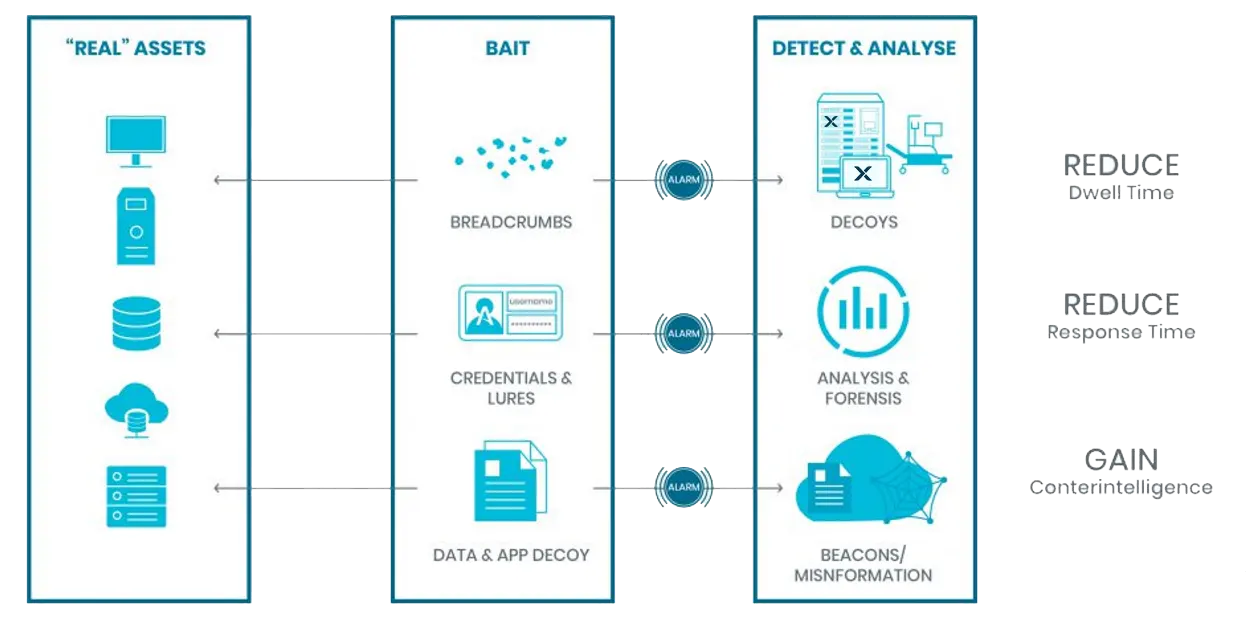
LMNTRIX Deceive is an advanced deception-based detection engine built into the LMNTRIX XDR platform. Instead of waiting for signature matches or behavioural anomalies, Deceive lays interactive traps and lures across your infrastructure—tricking adversaries into revealing themselves before they can cause harm.
By mimicking high-value assets like credentials, servers, shares, and cloud services, Deceive turns your network into a minefield for attackers. Every interaction with a deception artifact generates a high-confidence alert, empowering LMNTRIX analysts to rapidly investigate, contain, and respond — while the attacker is still in the early stages of the kill chain.
Why Traditional Defenses Fall Short?

Signature-based tools miss unknown threats

Behavioural analytics suffer false positives

Passive detection reacts too late — after compromise
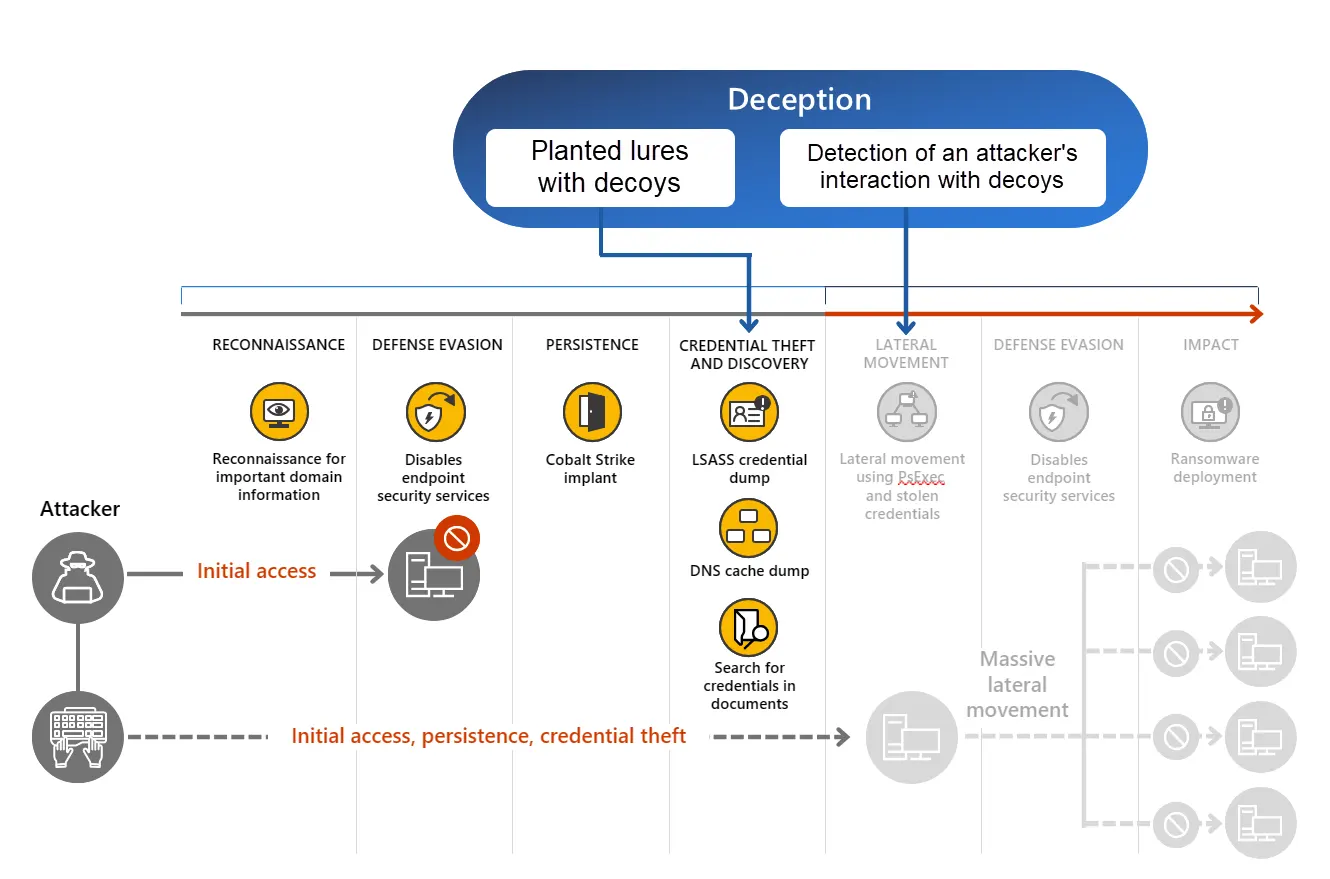
LMNTRIX Deceive flips the script — proactively engaging attackers during reconnaissance, credential harvesting, and lateral movement.
Key Benefits
- Detects attackers early — even advanced persistent threats (APTs)
- Prevents lateral movement and privilege escalation
- Reduces dwell time and alert fatigue
- Validates alerts with ground-truth interactions
- Enables proactive insider threat detection
- Zero impact on users, systems, or operations
What LMNTRIX Deceive Catches
| Attack Phase | Detection Technique |
|---|---|
| Reconnaissance | Fake AD objects, decoy file shares, lures |
| Credential Theft | Planted fake credentials in memory & cache |
| Lateral Movement | Interactions with decoy hosts, fake RDP/SSH |
| Insider Threats | User access to deceptive content or shares |
| Malware/C2 | Command-and-control triggers via decoy systems |
| Cloud Abuse | Fake S3 buckets and cloud service decoys |
Core Capabilities
Credential Deception
- Fake credentials placed in LSASS, browsers, and system memory
- Harvested by tools like Mimikatz, triggering silent alerts
Decoy Systems & Network Services
- Deployed across Windows/Linux environments
- Fully interactive: RDP, SSH, SMB, HTTP, MySQL, etc.
- Simulates real hosts with realistic artefacts
Deceptive Files & Shares
- Fake documents, databases, and mapped drives
- Interactions logged and correlated in real time
Breadcrumb Trails & Lures
- Mapped drives, shortcuts, and recent files guide attackers to decoys
- Creates irresistible paths for adversaries
Fake Active Directory Objects
- Nonexistent users, groups, and service accounts
- Detects AD enumeration and escalation attempts
Cloud & SaaS Deception
- Fake cloud buckets and apps (e.g., AWS S3, Azure, Google Drive)
- Ideal for hybrid and SaaS-heavy environments
Lateral Movement & Credential Misuse
- Flags unauthorized pivoting across systems
- Detects use of deceptive credentials anywhere in the domain
Built for XDR
Deceive is natively integrated into the LMNTRIX XDR platform, allowing:
Threat Correlation
Attack Path Visualization
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Analyst-Led Investigation & Response
Every interaction is validated by the LMNTRIX SOC
Remote containment actions initiated when needed
Why Deception Works
“Deception is immune to false positives because attackers must make the first move.”
– Carlo Minassian – Founder & CEO – LMNTRIX.
Unlike anomaly-based tools, LMNTRIX Deceive relies on attacker engagement. If an adversary touches a decoy, it’s a genuine threat. This results in ultra-high fidelity alerts, virtually eliminating alert fatigue for your SOC or our analysts.
Deployment at Scale
Automated rollout across endpoints, servers, and cloud
Zero user impact — fully passive and invisible
Supports hybrid, cloud, and air-gapped networks
Licensed per endpoint for predictable scaling
How It Works
- Deploy decoys mimicking real assets.
- Attackers interact, triggering alerts.
- Analysts investigate via XDR.
- Contain threats before damage.
Ready to Deceive and Defend?
Detect adversaries before they compromise your assets.
LMNTRIX DECEPTIONS FAQs
No jargon. Just straight answers on LMNTRIX Deceptions.
LMNTRIX Deceive
What is LMNTRIX Deceive?
LMNTRIX Deceive is a subscription feature of LMNTRIX XDR and an integral part of our Active Defense architecture. Our approach weaves a deceptive layer over your entire network – every endpoint, server and network component is coated with deceptions. The moment an attacker penetrates your network, they are in an illusive world where all the data is unreliable. If attackers cannot collect reliable data, they cannot make decisions. And if they cannot make decisions, the attack is paralysed. This approach provides the following benefits:
- No false positives – every alert is treated as a major incident and escalated to you
- Turn the tables on the bad guys!
- Change the economics of cyber defence by shifting the cost to the attacker
The intent of the service is to address insider threats and advanced human adversaries that are now on your network moving laterally stealing data and actively working to elevate their privileges. Existing solutions such as SIEM, IPS, EDR, Sandboxes, NextGen Firewalls, Web and Email Gateways are defenseless against this threat vector. By deploying deceptions everywhere, we are able to address this difficult threat vector.
LMNTRIX Deceive changes the asymmetry of cyber warfare, by focusing on the weakest link in a targeted attack – the human team behind it. Targeted attacks are orchestrated by human teams. And humans are always vulnerable. Advanced attackers rely on one simple fact – that what they see is real and that the data they collect is reliable. Firewall, Anti-virus, EDR, Sandbox, IDS, and intelligence feed technologies generate so much data that the signal is lost.
Attackers prowling a target network look for juicy content. They browse Active Directory for file servers and explore file shares looking for documents, try default passwords against network devices and web services, and scan for open services across the network.
LMNTRIX Deceive is a cloud-based service running off the LMNTRIX XDR where deceptions are deployed from, alerts reviewed, notifications configured and devices managed from.
LMNTRIX Deceive incorporates 4 types of deceptions. These are Decoys, Breadcrumbs, Tags, and Personas. Each is designed to address a different insider threat and human adversary threat type and together they form a powerful defense.

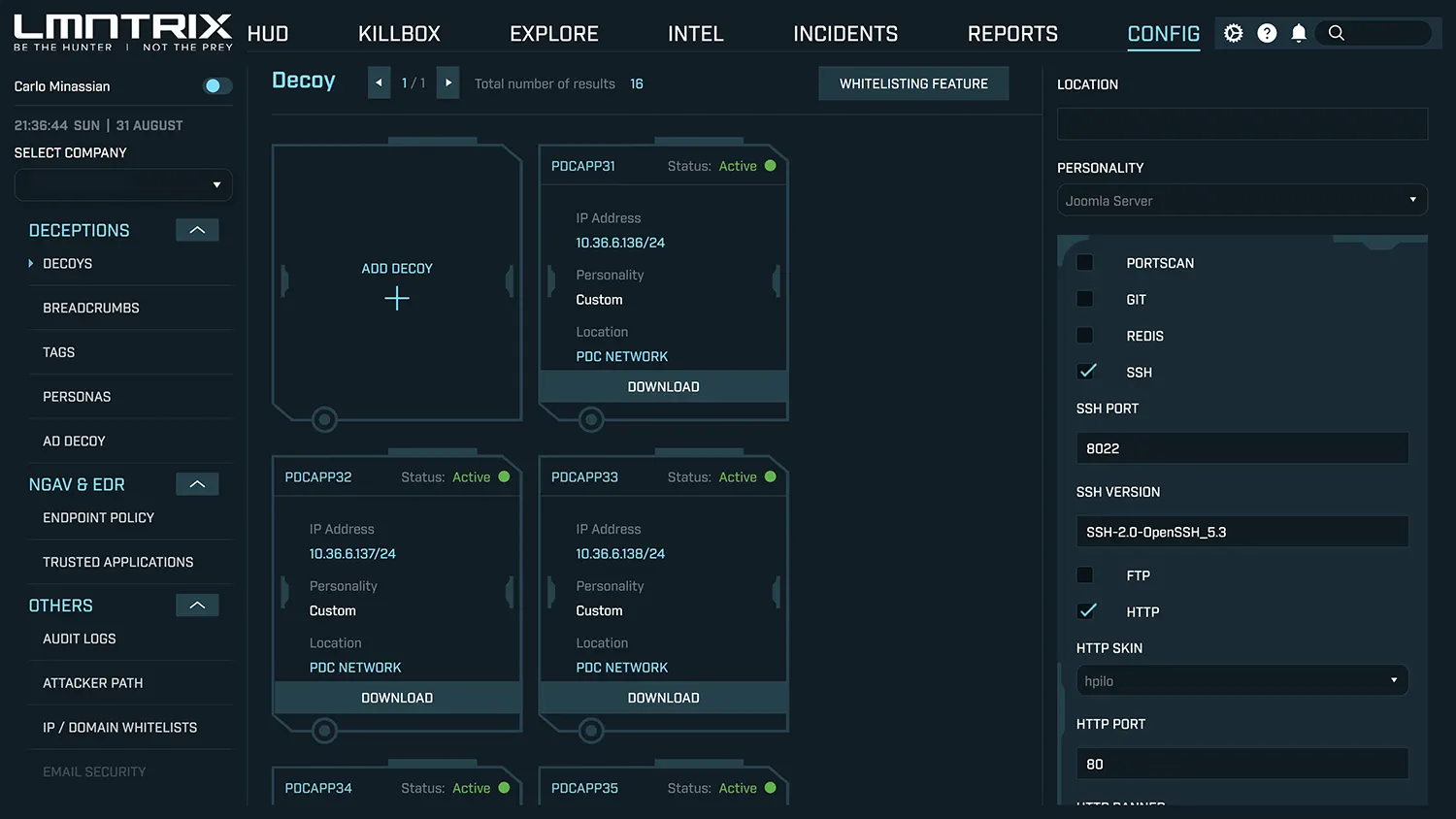
What is a Decoy?
Decoys are appliances that can represent one or more servers/services. These include operating systems, file servers, web servers, routers, switches, file shares with files, applications (NAS, FTP, SSH, etc). Decoys are available in appliance, VM or docker formats.
They are pre-configured and shipped to Customer’s to deploy on their networks. We recommend one per segment and one per 100 endpoints where budget permits. Each decoy communicates with the LMNTRIX Cloud for management and alerting.
Each Decoy is configured to match your existing network segment profile. For example, if you have a segment of Windows 7 desktops then we would deploy a Windows 7 Decoy amongst your existing fleet.
The deception capability offered by Decoys is to detect less sophisticated external adversaries and insider threats that are randomly conducting network reconnaissance and trying to gain access to customer’s network and data.
Whenever a Decoy is accessed (such as a network scan, ssh, ftp, file access, share access), an alert is captured by the LMNTRIX XDR and an incident created and investigated by the LMNTRIX CDC. Legitimate company employees should never have any reason to access a Decoy, as such every alert generated by a Decoy is treated as a high severity alert by the LMNTRIX CDC.
What services are supported by Decoys?
Each Decoy ships with 10 or more different types of detection modules. The Customer is responsible for selecting one or more detection modules within the Service Starter pack.
- Host port scan: Detects whether the Decoys were subjected to a port scan from a single originator. This feature can be disabled or enabled in the portal.
- Network port scan: Detects when an attacker scans across your network for a particular port. This requires multiple Decoys on your network
- FTP: Provides an authentication-only FTP daemon. All login attempts are recorded
LMNTRIX Mobile protects users and their devices from many types of threats. These threats are broadly categorized into Network, Device and Malware threats.

- SSH: Provides an authentication-only SSH daemon. All login attempts are recorded. A fake SSH session is presented to attacker.

- Telnet: Provides an authentication-only Telnet daemon. All login attempts are recorded. A fake Telnet session is presented to attacker

- HTTP brute-force: Exposes a web-based login page, and reports when login attempts are made. The HTTP module reports login attempts on a website hosted by the device. To make the login appear legitimate, we let you pick from a range of fake websites that might be found on internal networks. The skin only holds the login page. The device can be deployed as an endpoint running Apache services running on port 80.

- Windows shared files: Provides a fully functional Windows file share complete with actual files like PDFs, word files etc named by you. Alerts whenever someone tries to open the files. Includes the ability to join Active Directories.
Example: The device can be deployed as an endpoint running SAMBA services
When an attacker gains access to the database and attempts to click on a file he will be prompted to put in the password for the file and the alert gets triggered.

- Other Services: These include services like MySQL, Microsoft SQL server, HTTP proxy, SIP, SNMP, NTP, TFTP, VNC and Telnet which can be configured on the Decoys.
What is an AD Decoy?
Typically, on the top 5 list of adversary (APT or nation state) and red team techniques used once a point of breach is achieved is the enumeration of the Active Directory Radius service. The AD Decoy is a service that runs on each client AD server and alerts LMNTRIX when such activity takes place.
How does the AD Decoy work?
The AD Decoy queries the event viewer to find the logon events for normal users and Kerberos users for event IDs and shows the alerts on the LMNTRIX XDR for monitoring and response by the CDC
How is the AD Decoy deployed?
The AD Decoy deployment process is made up of the following 3 steps.
- The client AD Syd Admin needs to first manually create one or more fake users and fake SPN users on their AD server followed by the creation of fake SPN for various services that they wish to use. We recommend at least 5 fake users and SPN users.
- Next, the client needs to use the XDR (CONFIG Menu) and add all the fake user details from (1) above and save the settings to generate the AD Decoy. The fake user details are saved in an encrypted config file and added to the AD Decoy package ready for the client to download and deploy.
- The AD Decoy can now be deployed on AD server(s), and it runs as a windows service.
Please find the install/uninstall steps for this service enable in Windows AD Servers.
Pre-requisites: .Net Framework 4.0 or higher
AD server version: windows server 2012 and later.
Steps for installation :
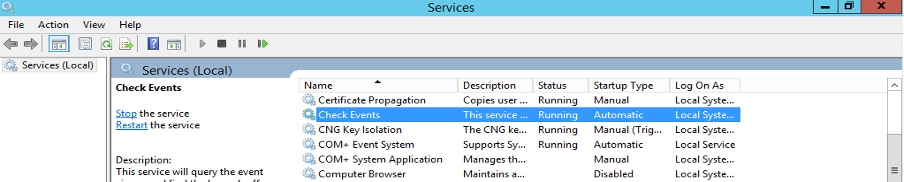
- Extract the CheckEvents.zip
- Open the command prompt in Administrator mode and redirect to the extracted folder path.
- Execute the below command to install the service on AD Server(s). Installer will copy the required files into C:\Program Files\CheckEvents folder and create the windows service.
InstallSvc.cmd i (Refer below image)

Once the installation is completed. “Check Events” windows service automatically starts and queries the logon events from the Event Viewer (Security Log). In the config file debug value is set to True so this service will generate the log file in the service installed folder. Debug file name format : debug_DDMMYYYY.log
Steps for Uninstallation :
- Open the command prompt in Administrator mode and redirect to the installer folder path.
- Execute below command to uninstall the service on AD Server. Installer will stop the service and remove the files from C:\Program Files\CheckEvents folder and delete the folder as well.
InstallSvc.cmd u (Refer below image)

What information is captured when an AD Decoy alert is triggered?
Any enumeration of Radius or login activity related to the fake users or SPN users generates a deception threat alert on the XDR with the details below.

Are all Decoy alerts communicated to clients?
The LMNTRIX CDC will not alert you on every alert triggered by a Decoy. Instead, we aggregate related events to form a single incident. For example, if an attacker launches a brute-force attempt against your FTP server, you want to receive a single alert about the attack, not one per username tried.
Incidents are defined as duplicated events from the same source against the same target service within a period.
The LMNTRIX XDR records every single event generated by decoys and made available for forensic investigations irrespective of the amount of detail reported in an incident record.
What is a Breadcrumb?
A Breadcrumb refers to a small, subtle piece of false information or data that is intentionally placed within a system to lure or mislead attackers. These Breadcrumbs are part of our broader deception strategy designed to divert attackers towards a Decoy system (a honeypot) or to provide misleading intelligence.
For example, Breadcrumbs can be fake credentials, misleading file names, or false configurations that lead attackers to believe they are accessing valuable resources. When an attacker interacts with a Breadcrumb, it triggers monitoring and alerts defenders, giving them insights into the attacker’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
The goal is to increase the complexity of the attacker’s task while gathering intelligence without risking actual assets. This technique is often used to complement more traditional security measures, adding a layer of misdirection to protect sensitive information and infrastructure.
How are Breadcrumbs deployed?
Breadcrumbs are deployed across all Customer endpoints (servers and desktops). Each endpoint is populated with multiple interesting breadcrumbs to increase the chances of fooling attackers. Once an attacker takes a bait (breadcrumb) and tries to communicate with a breadcrumb, they are directed to the LMNTRIX XDR where they are monitored by our intrusion analysts as they communicate with our Decoy platform as we record all their actions.
Breadcrumbs rely on the integration of LMNTRIX XDR with Customer’s Active Directory for breadcrumb deployment. There are no agents or software deployed on endpoint, only interesting breadcrumbs, such as fake Admin accounts, saved Usernames/Password, and web browsing history. The breadcrumb deployment process takes less than 300 milliseconds and for windows machines which are a part of Active directory, we use legitimate API calls for breadcrumb deployment and for Linux machines which are not integrated with Active directory, we use SSH to deploy deceptions on those machines.
The process is repeated once a month to ensure breadcrumb persistence.
How do Breadcrumbs work?
During an advanced attack, an attacker gains access to an endpoint without knowing where that endpoint sits in the network structure. The attacker employs a range of tools to iteratively discover the network hierarchy from that endpoint. The collected information is analyzed to plan access attempts to lateral network locations. The goal of the attack is to locate sensitive information such as confidential company data.
The agentless solution offered by LMNTRIX presents attackers with a deceptive network view, exploiting the attacker’s belief that all received data is valid. Limitless enticing deceptions detect and divert an attack, immediately gathering information about the attacker’s ongoing activity when access is attempted, without the attacker’s awareness. Superior technology, real-time source-based forensics, and intimate knowledge of cyber-attacker psychology ensures visibility of attacks and returns information-control to the network administrators.
The following are the 3 phases on how breadcrumbs work:
- Deceive: We deploy Breadcrumbs on Client endpoints using the LMNTRIX XDR. Connectivity between the client network and LMNTRIX XDR is secured using IPSec VPN.
- Detect: Attackers take the bait (Breadcrumbs) and expose themselves.
When an attacker lands on a specific endpoint, he runs his reconnaissance tools to get a better understanding of the Clients network and gain access to such things as credentials, servers, systems and applications. However, what he ends up gaining access to are actually our Breadcrumbs including cached information that we have setup for him to interact with. During this interaction, the attacker is redirected off the Client network and onto the Decoy. The Deception is designed in such a way that the attacker thinks he’s interacting with a real server, system or application as the deception is setup to mimic an actual environment. - Defeat: Alert and investigate attack profile
LMNTRIX XDR then interacts with the attacker and the compromised endpoint machine to take snap shots from it. Complete forensic information is recorded and made available to the CDC for further analysis.

What is the impact of deploying Breadcrumbs on our network or on our machines?
Once our Breadcrumbs are deployed, they have minimal impact on your network, applications and users. The following provides the impact of breadcrumbs on your end-users, IT and attackers:
- Attackers: Our Breadcrumbs consist of data that appears to be a legitimate for the attacker, but is isolated and monitored, and that seems to contain information or a resource of value to attackers.
- End users: Our Breadcrumbs are not visible to the end users after its deployed on the endpoints and if in case the end user sees the Breadcrumb and uses it, then a false positive is triggered at out CDC. Our claim is that we have near 0 false positives.
- IT: Also, IT would not have access to view the breadcrumbs because this is not deployed on the network

What categories of Breadcrumbs do you offer?
Following is a list of Breadcrumbs that LMNTRIX takes advantage of. There are 11 categories in total and each one generates an alert to our CDC when tripped.
- Browsers: The browser’s Breadcrumbs produces deceptive information relating to the domain webhosts. Browser History deceptions masquerade as web servers that valid users have accessed in the past and this information in stored in the Google Chrome Database on the endpoint. The breadcrumbs added here tempt an attacker to access a customized webpage for Synology NAS Login. Alerts are triggered and sent to the CDC when an attempt to access a deceptive web server is made

This is a highly interactive service running on the breadcrumb server and this produces 2 alerts.
The first alert is sent when someone accesses the webpage
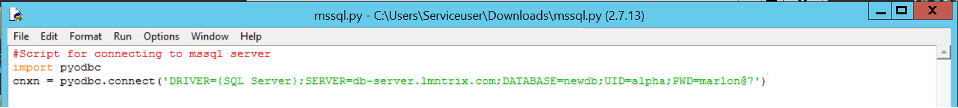
- Databases (Mysql and Mssql): The Database Breadcrumbs produces deceptive information relating to domain databases. Alerts are triggered when attempts to access deceptive domain databases is made.
The demo can be shown by trying to interact with the ports 3306(Mysql) and 1433(Mssql) using python.

- FTP: The FTP Breadcrumb produces deceptive information relating to domain file servers. Incident alerts are triggered by attempts to access deceptive file servers
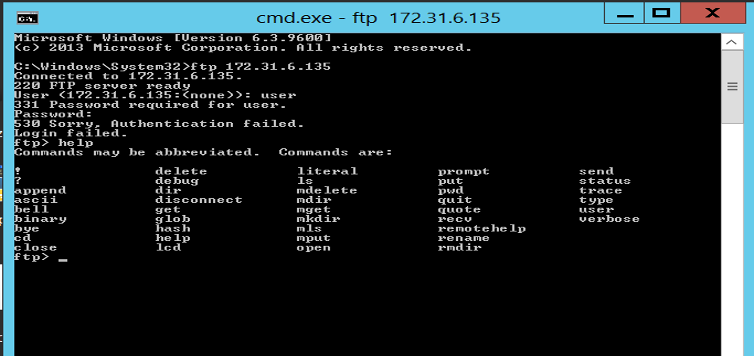
The session is highly interactive and from the screenshot above, it clearly shows that all the commands that’s a part of the FTP protocol family.
- RDP: The RDP Breadcrumb plants deceptions that are related to local RDP files. A remote desktop protocol (RDP) file is used to access one endpoint from another. Incident alerts are triggered by attempts to use planted RDP files to access deceptive servers

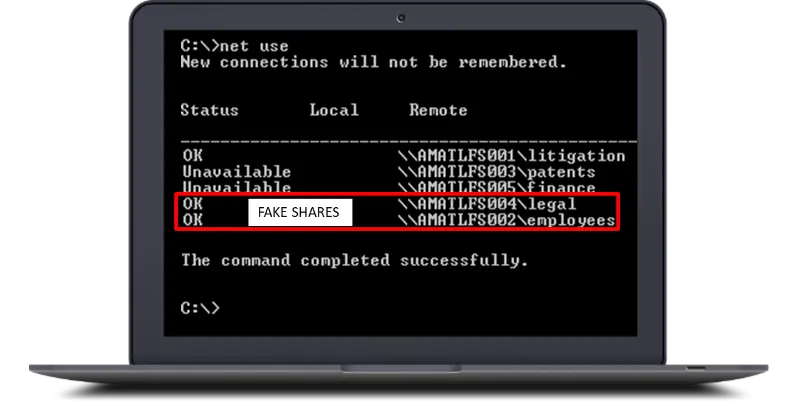
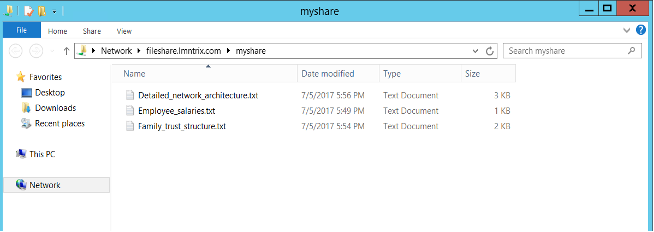
- Shares: The Shares Breadcrumb produces deceptive information relating to shared folders within the domain. Incident alerts are triggered by attempts to access a deceptive shared folder.
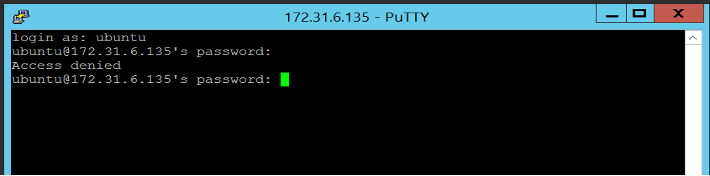
- SSH: The SSH Breadcrumb produces deceptive information relating to domain SSH servers. Incident alerts are triggered by attempts to access a deceptive SSH server.
- Saved Sites (HTTP) in Windows Vault – Saved Site deceptions masquerade as password-protected web servers and the credentials required for authentication.

- Telnet: The SSH Breadcrumb produces deceptive information relating to domain Telnet servers. Incident alerts are triggered by attempts to access a deceptive Telnet server.

- VNC: Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop sharing system that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. It transmits the keyboard and mouse events from one computer to another, relaying the graphical screen updates back in the other direction, over a network
The VNC Breadcrumb produces deceptive information relating to servers which can be accessed to the VNC service. Incident alerts are triggered by attempts to access the breadcrumb server.

What are best practices for deployment of Breadcrumbs?
On Windows desktops, we recommend the use of the following breadcrumbs:
- Saved Sites in Windows Vault: We recommend this because, this breadcrumb saves fake domain credentials in the vault of a windows machine and produces deceptive information about the Operating System.
- RDP & VNC: This is a common service/tools used by network administrators for support and as such it makes for a great trap for attackers
- Shares: Recommended on a windows machine which as it creates deceptive recently accessed file shares in the recent directory.
On Linux Servers, we recommend the use of the following breadcrumbs:
- SSH and Telnet: Since these services are active on most Linux Servers for administrative purposes, we recommend deploying these Breadcrumbs on Linux Servers.
- FTP: FTP service is common service in a Linux environment.
- Shares: If your environment uses Samba services, its highly recommended to use this service to create fake user shares.
Recommended Breadcrumbs common for both platforms
- Browser: This is recommended across both Linux and windows platforms since passwords are regularly saved by users in browsers and presenting an extra set of fake credentials to an attacker increases the probability of an attacker being lured to use the fake credentials.
- Databases: Recommended on both platforms as they can be accessed from both environments.
How do I configure users with Breadcrumbs?
To access a domain, LMNTRIX requires the details of two different users in your user directory
DIRECTORY USER: LMNTRIX uses the directory user to navigate your user directory
- To create the directory user account
- In the user directory, assign search-only permissions to a user
SERVICE USER: LMNTRIX can use the service user to deploy deceptions on network hosts
- In the user directory, create a new user.
- In the domain to be managed, make the user a local administrator on all endpoints
- Set the user attribute Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated to TRUE.
- Configure the service user to read event logs from Domain Controllers
Note: In each supported AD domain, the Local Admin AD group must be created in the domain Builtin container.
Set the user attribute Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated to TRUE
What are Tags?
Tags are unique tags that are embedded in a variety of places such as in documents, emails, Linkedin, bitcoin, images, databases, etc. that nobody should be accessing. They have the same profile and naming conventions as that used by the customer. If anyone accesses them then an alert is sent to the LMNTRIX XDR and for our intrusion analysts to investigate and escalate to the Customer if necessary. Tags can include files or emails within SaaS platforms such as Office365, Dropbox, Google Drive, HipChat, Slack, etc to monitor the vendor engineers accessing Customer files.
The use of Tags as a form of Deception deployed on real assets (workstations and servers) is aimed at detecting attackers both internal and external to the organization that have gained actual access to the Customer assets. Furthermore, Tags is one of the few methods that allows LMNTRIX to get close to confirming attack attribution. Unlike Breadcrumbs that rely on Decoys for alerting, Tags generate alerts independent of Decoys.
What types of Tags are available?
Tags are a “quick, painless way to help defenders discover they’ve been breached (by having attackers announce themselves).” To accomplish this, we create tags such as:
- A URL an adversary might visit
- A domain or hostname an adversary might resolve
- A Word or PDF document an adversary might open
When the intruder accesses or makes use of the tag, LMNTRIX will notify you via email and share a few details about the event in the form of an incident.
Web Tags
These are unique URL tags that are triggered whenever someone requests for a URL.
They are deployed in the form of an email subject line in your emails, embedded as a tag in some of your documents and as a tag in the form of a password.html files.
Best Practices:
- You could send yourself an email with the Webbug tag.
- In an email with a juicy subject line. So, if your emails are stolen, then an attacker reading them should be attracted to the mail and visit the link.
- Embedded in documents.
- Inserted into your company’s webpages that are only found through brute-force
- This URL is just an example. Apart from the hostname and the actual tag (the random string), you can change all other parts of the URL
Here is an example of a Webbug tag that we deploy for our Customer’s and the alert that we receive at the Cyber Defense center.
http://lmntrixtags.us/articles/tags/static/57wv83vsr0gskmwssixedeth7/index.html

DNS Tags
DNS Tags are unique hostnames that gets triggered whenever an attacker performs a lookup on your domain.
Best Practices:
- Create this in a .bash_history, or .ssh/config, or ~/servers.txt
- Include in a PTR entry for dark IP space of your internal network. Quick way to determine if someone is walking your internal DNS without configuring DNS logging and monitoring.
- We create an extremely simple bridge between a detection and notification action. There are many possibilities, one of them is to tail a logfile and which in turn triggers the tags when someone logs in and our CDC will receive an alert.
- Use as the domain part of an email address.
Here is an example of a DNS tag that we deploy for our Customer’s and the alert that we receive at the Cyber Defense center.
j64qemw57le0pf7s688cp547q.lmntrixtags.us

We provide SMTP tags to monitor any attacks on your databases with a unique email address
Best Practices:
- Drop this unique email address on your databases with user’s information and if an attacker tries to send an email to the email address, our CDC will receive an alert
- Here is an example of a SMTP tag that we deploy for our Customer’s and the alert that we receive at the Cyber Defense center.
- In a database with a USERS table, drop a fake record in there with this email address. If it gets triggered, you know someone has accessed your data.

We deploy unique QR codes and this is used as a tag on your containers which are left in secure locations.

As soon as the QR code is scanned, the attacker is prompted with a tag link and once he clicks on it, our CDC receives an alert and we would be able to provide our Customer with the location of these containers.
Best Practices:
- Place these QR codes on devices, computers, printers etc which are in a secure location. We will notify you through an email incase these are scanned.
- Use this QR Code to tag a physical location or object
- On your desk
Here is an alert that our analysts at the CDC receive.

MS Word and Adobe Acrobat Tags
We deploy a tag in the form of a word file or a pdf file in any of the Customer’s servers. As soon as the attacker opens this file for editing, an alert is triggered and our analysts at the CDC start investigating it before the attacker even realizes that he is being monitored.
Best Practices:
- You can add these files into the Windows directory Tags as an additional layer of deception.
- You can rename the document without affecting its operation
- These files can be saved on network shares and does not require any additional software for configuration.
- Attach to an email with a tempting Subject line
- Simply placing a tag in the document meta-data, gives us a reliable ping when the document is opened
Leave these files on a web server in an inaccessible directory, to detect webserver breaches.
Here is an example of MS word tag that we deploy for our Customer’s.
Here is an alert that our analysts at the CDC receive

Here is an example of Adobe Acrobat tag that we deploy for our Customer’s
Here is an alert that our analysts at the CDC receive.

SQL Server Tags on SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE
Webservers often draw active content from a datastore that is usually a SQL database, and these are quite hard to protect and harden. Hence why SQL databases are likely to be exploited by SQL injection attacks.
With our SQL tags, alerts are triggered to our CDC when any one of these commands are executed on the SQL database. This adds an additional layer of security to the Customer’s databases. The next step is to copy the SQL snippet and run in your SQL Server database.
Here is an alert that our analysts at the CDC receive.

Best Practices:
- It isn’t natively possible to have MSSQL server trigger an action on a SELECT statement, but what you can do is create a custom VIEW which triggers a DNS query when a SELECT is run against the VIEW.
- Deploy a SELECT or INSERT or UPDATE or DELETE tags with a tempting VIEW name such as USER_DETAILS.
Windows Directory Browsing Tags
Our CDC gets notified whenever an attacker opens or browses a Windows directory in Explorer. It works with network shares and doesn’t require any additional software.
Additional interesting file tags are added which you think would be a risk if it falls into the wrong hands.

Best Practices:
- Windows provides an even cooler way to get notified, in the guise of the venerable old desktop.ini configuration file. Dropping a desktop.ini file in a folder allows Explorer to set a custom icon for a file.
- Since this icon can reside on a remote server (via a UNC path), using DNS we can effectively make use of a tag as our icon file.
- You can add additional files into the directory. So, you can combine other tags like MS word tag and Adobe Acrobat tag files in the directory.
Our CDC gets notified whenever an attacker has cloned your webpage.
Place this JavaScript on the page you wish to protect. When an attacker clones your site, they’ll include the JavaScript. When the JavaScript is run, it checks whether the domain is expected. If not, it fires the tag and the CDC will receive an alert.
Here is an example of a Cloned Website tag that we deploy for our Customer’s.
if (document.domain != “example.com”)
{var l = location.href;
var r = document.referrer;
var m = new Image();
m.src = “http://lmntrixtags.us/”+
“8oedbi0nvs408y049i47f3ubo.jpg?l=”+
encodeURI(l) + “&r=” + encodeURI(r);
}
Here is an alert that our analysts at the CDC receive

Best Practices
- Run the script through an obfuscator to make it harder to pick up.
- Deploy on the login pages of your sensitive sites, such as OWA or tender systems.
- This Tag does not support content delivery networks (CDN). Clients running websites behind a CDN should not use this Tag.
Our CDC gets notified whenever an attacker clones the SVN repo. Don’t forget to run “svn commit “after you’ve added the tag.
Here is an example of a SVN tag that we deploy for our Customer’s.
svn propset svn:externals “extras http://wv3c56dkki3yo27e8zhbc7n88.lmntrixtags.us” .
Here is an alert that our analysts at the CDC receive

Our CDC gets notified whenever an attacker uses this credential pair to access AWS programmatically (through the API). The key is hyper unique. i.e. There is 0 chance of somebody having guessed these credentials. If this tag fires, it is a clear indication that this set of keys has “leaked”.
Here is an example of an AWS tag that we deploy for our Customer’s.
[Default]Access key Id: AKIAIQ7YPSXLN3BH2CKQ
Secret Access Key: 0QHPJnXl1dwqUsjrh2voTOLMMLH2V8ft98iFiVoM
Here is an alert that our analysts at the CDC receive
Best Practices
- These credentials are often stored in a file called ~/.aws/credentials on linux/OSX systems. Generate a fake credential pair for your senior developers and sysadmins and keep it on their machines. If an attacker tries to access AWS with the pair you generated for Bob, chances are that Bob’s been compromised.
- Place the credentials in private code repositories. If the tag is triggered, it means that an attacker is accessing that repo without permission
The tag is like the Web tag, however, when the link is loaded the view will be immediately redirected to the specified redirect URL.
Here is an example of an Fast Redirect tag that we deploy for our Customer’s.
http://lmntrixtags.us/articles/feedback/xqmtoyuxa0vs0to66p5fofu6h/post.jsp

Best Practices
- Replace links with these to capture user information before user is redirected to where they want to go.
- Embedded in documents.
- Inserted into LMNTRIX webpages that are only found through brute-force.
- This URL is just an example. Apart from the hostname and the actual tag (the random string), you can change all other parts of the URL.
The tag is like the Fast Redirect tag, however, when the link is loaded the user’s browser / browser plugin information is captured.
Here is an example of an Slow Redirect tag that we deploy for our Customer’s.
http://lmntrixtags.us/images/uuadczrsng7apwu468df28jf1/submit.aspx

Best Practices
- Replace links with these to capture user information before user is redirected to where they want to go.
- Embedded in documents.
- Inserted into LMNTRIX webpages that are only found through brute-force.
- This URL is just an example. Apart from the hostname and the actual tag (the random string), you can change all other parts of the URL.
What geolocation information about the attacker do Tags provide?
We provide the clients with the geographical location associated with the hosting device. This varies depending on the type of tags that the attacker use.
- If the attacker uses a tag that works on DNS protocol, we provide our clients with the DNS information of the attacker.
- If the attacker uses a tag that works on HTTP protocol, we provide our clients with the Source IP information of the attacker.
- If the attacker uses a tag that works with SMTP protocol, we provide our clients with the mail servers location and other details which would include the Email address of the attacker, Email attachments etc.
- LMNTRIX Tags provides us with the Internet service provider information, Hostname, Useragent used, IP address, date and time of the attack etc, so that we can track the attacker down quickly and attribute the attack, not possible with any other solution. Furthermore, Tags notify us if the Known Exit Node was from a Tor network.

What are Personas?
Personas are unique accounts and profiles created across the Customer systems, applications and social media channels. Whenever contact is made with one of them via email, we know that an adversary has stolen or is targeting the respective data.
LMNTRIX simply guides the Customer through the process of creating Personas. It’s the Customer that creates all of the Personas across their systems as they’re the only one who has access to them.
Following provides examples of identities clients generally deploy:
- 5 Linkedin personas/fake profiles with email addresses. Social media identities are a great way to identify Customer employees are being poached or a target of a phishing/spam campaign.
- 5 different Email accounts within the Customer email/exchange directory addresses.
- 5 different Users/Email addresses created within the Customer’s “Customer Database” (E.G. salesforce.com/CRM). Any emails to these shows that the Customer’s customer DB has been stolen.
- 5 different Users/Email addresses created within the Customer HR application. Any emails to these shows that the Customer employee details have been leaked/stolen.
- 5 identity decoy phone numbers in the Customer phone directory.
- 5 Active Directory identities that can be monitored.
- 5 Customer specific application identities that can be monitored such as Marketing and Accounting systems
You must take great amount of effort to ensure that all social media decoys are realistic. For example, the following should be your approach for LinkedIn:
- Create 5 new employee profiles on LinkedIn. They must all look legitimate with proper work/company history. Their email addresses match that of other employees, such as firstname@customerdomain.com. Customer then creates aliases for these forwarding them to our CDC.
- At minimum, all employee profiles should have 10 yrs work history. You can use a new name but copy designation and employee history from other employees or competitors.
- Ensure that their location is consistent with where you operate.
- Finally, invest sometime on each profile making connections with people in your industry.
What are prerequisites & customer responsibilities for setting up LMNTRIX Deceive?
The LMNTRIX Deceive Starter Pack is required to be completed by the customer prior to service establishment.
- The Customer is responsible for the accurate completion and selection of the Starter Pack that includes each decoy profile, detection modules, decoy name and other details required for each detection module.
Note: Please choose a Decoy name such that it suits each Decoy Personality.
- The Customer is responsible for the correct deployment and network interconnectivity of each Decoy which includes updating the Starter Pack with information related to the IP address, subnet mask, VLAN, default gateway IP address etc of the decoy.
- The Customer is responsible for the accurate matching of Decoy detection modules to each network segment asset profile.
- The Customer is responsible for the correct DNS entries in their internal DNS server for each Decoy detection module to accurately resolve IPs to meaningful names, E.G. research.companyname.com
- In case of damage to the Decoy, please notify us at CDC@lmntrix.com.
- The Customer has to define the number of subnet ranges in which the Tags are deployed.
- The Customer is responsible for making sure the Tags provided are placed exactly in the same subnet as specified by them in the pre-requisites.
- A Unique Name that the customer provides us with, as per the Starter Pack must be related to the subnet in which the Tag is placed so we can identify the source of the trigger and alert you of the same.
- One comment/subnet must be specified so that we can remind you where you would have used the Tags.
- The IP ranges of the subnets must be updated in the Starter Pack.
- The OS used by the Endpoints must be specified.
- The type of Tags required must be specified by the Customer.
- If the Tags are placed in incorrect subnets, we would not be able to track the attack effectively and it would likely cause confusion.
- The Customer must create their own Tag DNS entries such that their Tags domain points to the LMNTRIX domain. This is to ensure that the attacker is never exposed to the LMNTRIX brand or domain and cause any suspicion for the attacker not to click on a tag.
Example: The customer can create a web bug http://xyzcompany.com/images/4y26grc4sx168ts7fh9zh84k0/contact.php and point it to http://lmntrixtags.us/images/4y26grc4sx168ts7fh9zh84k0/contact.php in their DNS
- Once we receive the updated Starter Pack form from the Customer, Tags are sent to the Customer through an email, so that they can be deployed in their environment.
- In case the Customer loses their Tags, they may email the CDC@lmntrix.com with their Unique name, Subnet information, and Company name, so that we can resent the Tags to them.
- If the Customer requires new Tags, they can email the CDC@lmntrix.com with an updated Starter Pack so that we can prepare and send them the new tags.
- The Customer is responsible for the accurate completion and selection of their breadcrumb profiles for every Organizational Unit (OU).
- On all Windows hosts, allow the LMNTRIX XDR to execute commands by Enabling File and Printer Sharing
- Enable LMNTRIX to test host connections by ensuring ICMP ping requests are enabled on the network.
- Customer should update the Starter Pack after creating the Directory user and Service user in their domain as mentioned in the Configuring Users section of this document.
- Enable default deployment by ensuring that the LMNTRIX XDR is a member of the network domain.
- The operating system of the workstations in each segment must be identified and updated on the Starter Pack by the Customer.
- The Customer is responsible for the selection of Breadcrumbs suitable for each segment. The Customer can refer to Best Practices for Deployment of Breadcrumbs-Recommended
- The Customer is responsible for the Breadcrumb-to-Decoy design and stories. E.G. All workstations will have a Shares Breadcrumb pointing to the research.companydomain.com, etc.
Breadcrumbs Remote operation method
By default, Breadcrumbs are deployed on hosts from the LMNTRIX XDR using the Sysinternals Deployment Tool (psexec). If your environment does not support this default configuration, you can select to run the Breadcrumbs setup tool on each host manually or deploy Breadcrumbs using a third-party remote-management tool that requires some configuration on the tool’s server (i.e. SCCM/Tanium/PatchLink/BigFix).
Note: You can select only one deployment method.
Configuring Integrated Operational Methods
The LMNTRIX remote-operation method handles Windows policy deployment and forensics collection.
The below tool can be configured to run LMNTRIX operations via the LMNTRIX’s Cloud.
- Sysinternals Deployment Tool
The Windows Sysinternals Suite is a Microsoft freeware tool that enables host management. For details, see the Sysinternals Utilities Index.
By default, the Sysinternals deployment tool runs LMNTRIX operations
External Operational Method
We can configure policy-deployment to be managed by a third-party tool directly. Windows hosts can be managed via tools such as Microsoft SCCM while Linux hosts can be handled by any external tool, such as Ansible.
- Customer is responsible for the creation of unique email accounts in their mail server and have these forwarded to the LMNTRIX CDC.
- Customer is responsible for the creation of unique personas/profiles in their applications including CRM/Salesforce, HR, Accounting, Marketing, and Active Directory environments and update that in the pre-requisites form.
- Customer’s is responsible for the creation of the LinkedIn personas and respective email and redirection to the LMNTRIX CDC.
- Customer’s need to create aliases for the above mentioned unique email addresses so that when an email is sent, it will be forwarded to alerts@lmntrix.com.
Related Resources

Customer Story: AFG
Mid-tier financial services firm turns the tables on the hackers and gains context to improve security decision-making while enhancing security protection in every business system

Deception Technology Guide
White Paper
How We Protect
small and large enterprises
Why clients love working with LMNTRIX
You’re ready for advanced protection
and that means XDR







Don't just take our word for it...

Leader

Leader

Open Source Excellence

Top 250 MSSP Companies In The World

Users Choice Award
Top Rated Security



Ready to take the next steps with LMNTRIX MXDR ?
The choice is yours: see LMNTRIX in an on demand demo or set up a customized demo or request a quote.






